Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (1): 66-71.doi: 10.24920/003788
• Case Report • Previous Articles Next Articles
An Insight of the First Community Infected COVID-19 Patient in Beijing by Imported Case: Role of Deep Learning-Assisted CT Diagnosis
Dasheng Li1, *( ), Dawei Wang2, Nana Wang1, Haiwang Xu1, He Huang1, Jianping Dong3, Chen Xia2
), Dawei Wang2, Nana Wang1, Haiwang Xu1, He Huang1, Jianping Dong3, Chen Xia2
- 1Department of Radiology, Beijing Haidian Section of Peking University Third Hospital (Beijing Haidian Hospital), Beijing 100080, China
2Institute of Advanced Research, Infervision Medical Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing 100025, China
3Department of Infection, Beijing Haidian Section of Peking University Third Hospital (Beijing Haidian Hospital), Beijing 100080, China;
-
Received:2020-05-28Accepted:2020-07-16Published:2021-03-31 -
Contact:Dasheng Li E-mail:724501143@qq.com
Cite this article
Dasheng Li,Dawei Wang,Nana Wang,Haiwang Xu,He Huang,Jianping Dong,Chen Xia. An Insight of the First Community Infected COVID-19 Patient in Beijing by Imported Case: Role of Deep Learning-Assisted CT Diagnosis[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(1): 66-71.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Table 1
Summary of pulmonary lesions of the first imported COVID-19 patient in Beijing interpreted by a DL-based diagnostic system"
| Lesion No. | Location | Density type | Volume a (mm3) | Alerts | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First visit | Second visit | Alteration b | ||||
| 1 | APLU | Solid | ND | 8.41 | + | / |
| 2 | APLU | Solid | 35.83 | 39.34 | + | / |
| 3 | ARU | Solid | ND | 3.98 | + | / |
| 4 | ARU | Solid | 9.03 | 14.76 | + | / |
| 5 | ARU | Solid | 17.97 | 21.27 | + | / |
| 6 | ARU | Solid | 9.07 | 5.28 | - | / |
| 7 | APLU | Solid | 10.24 | 23.03 | ++ | / |
| 8 | AnRU | GGO | ND | 10.40 | ++ | / |
| 9 | AnRU | Solid | 9.00 | 7.09 | - | / |
| 10 | APLU | Solid | ND | 13.60 | + | / |
| 11 | AnLU | Solid | ND | 11.53 | ++ | / |
| 12 | DRL | Solid | ND | 20.38 | ++ | / |
| 13 | DLL | Solid | 5.97 | 4.21 | - | / |
| 14 | PRU | Solid | ND | 4.85 | + | / |
| 15 | PBRL | GGO | ND | 606.17 | +++ | / |
| 16 | PBLL | Solid | ND | 11.06 | ++ | / |
| 17 | Interlobular | Solid | ND | 16.28 | ++ | / |
| 18 | MBRL | GGO | 309.42 | 140.04 | - - - | Suspected Pneumonia |
| 19 | MBRL | SM | ND | 4713.95 | ++++ | Suspected Pneumonia |
| 20 | MRM | Solid | 3.47 | 6.65 | + | / |
| 21 | PBRL | SM | 105.08 | 7784.19 | ++++ | Suspected Pneumonia |
| 22 | PBRL | GGO | ND | 46.98 | ++ | / |
| 23 | LBRL | GGO | ND | 35.46 | ++ | / |
| 24 | MBRL | GGO | ND | 215.55 | +++ | Suspected Pneumonia |
| 25 | PBRL | GGO | ND | 202.37 | +++ | / |
| 26 | PBRL | GGO | ND | 54.07 | ++ | / |
| 27 | PBRL | SM | 34.17 | 5136.25 | ++++ | Suspected Pneumonia |
| 28 | PBRL | GGO | ND | 32.30 | ++ | / |
| 29 | PBRL | SM | ND | 4821.64 | ++++ | Suspected Pneumonia |
| 30 | LBRL | mGGO | ND | 207.56 | +++ | Suspected Pneumonia |
| 31 | LBRL | GGO | ND | 43.72 | ++ | / |
| 32 | APLU | Solid | 17.11 | ND | NA | NA |
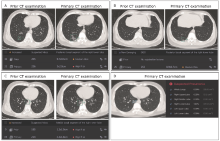
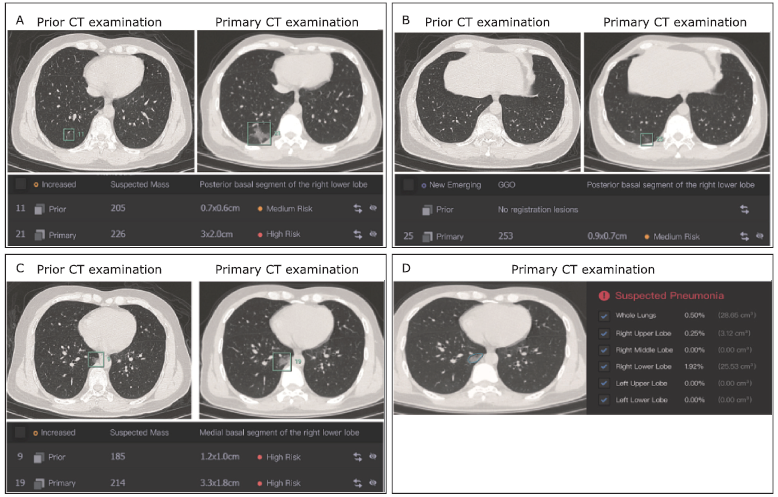
Figure 1.
Image findings of a COVID-19 patient analyzed using deep learning (DL)-based CT diagnostic systems. (A) Ground glass opacity nodular detected on the prior CT scan developed to pneumonia-like lesions on the primary CT scan. The DL-based diagnostic system (CT Lung) detected it and quantitatively monitored the growth. (B) A new nodule on the primary CT scan was alerted as medium risk for malignancy. (C) A ground glass opacity detected in the medial basal segment of the right lower lobe on the primary CT scan was automatically registered and compared with the prior one quantitatively, with a significant volume increase to 15.68 times, which suggested the rapid development pattern of inflammatory lesion. (D) The DL-based diagnostic system (CT Pneumonia) alerted the lesion in (C) as a suspected COVID-19 lesion on the primary CT scan, which was consistent to the diagnosis by the CT Lung system. Its volume proportions of the whole lungs and of the selected pulmonary lobes were calculated."
| 1. |
Cucinotta D, Vanelli M. WHO declares COVID-19 a pandemic. Acta Biomed 2020; 91(1):157-60. doi: 10.23750/abm.v91i1.9397.
doi: 10.23750/abm.v91i1.9397 pmid: 32191675 |
| 2. |
Li DS, Wang DW, Dong JP, et al. False-negative results of real-time reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2: Role of deep-learning-based CT diagnosis and insights from two cases. Korean J Radiol 2020; 21(4):505-8. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2020.0146.
doi: 10.3348/kjr.2020.0146 pmid: 32174053 |
| 3. |
Li XM, Zeng WB, Li X, et al. CT imaging changes of corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a multi-center study in Southwest China. J Transl Med 2020; 18(1):154. doi: 10.1186/s12967-020-02324-w.
doi: 10.1186/s12967-020-02324-w pmid: 32252784 |
| 4. |
Yoon SH, Lee KH, Kim JY, et al. Chest radiographic and CT findings of the 2019 novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19): Analysis of nine patients treated in Korea. Korean J Radiol 2020; 21(4):494-500. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2020.0132.
doi: 10.3348/kjr.2020.0132 pmid: 32100485 |
| 5. |
Ng BH, Nik NN, Yu-Lin AB, et al. Lung computed tomography patterns of a cluster of asymptomatic young males with COVID-19 admitted to a teaching hospital in Kuala Lumpur. Med J Malaysia 2020; 75(4):368-71.
pmid: 32723996 |
| 6. |
Wang YR, Liu YX, Liu L, et al. Clinical outcome of 55 asymptomatic cases at the time of hospital admission infected with SARS-Coronavirus-2 in Shenzhen, China. J Infect Dis 2020; 221(11):1770-4. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiaa119.
doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiaa119 pmid: 32179910 |
| 7. |
Hu ZL, Song C, Xu CJ, et al. Clinical characteristics of 24 asymptomatic infections with COVID-19 screened among close contacts in Nanjing, China. Sci China Life Sci 2020; 63(5):706-11. doi: 10.1007/s11427-020-1661-4.
doi: 10.1007/s11427-020-1661-4 pmid: 32146694 |
| 8. |
Chen ZH, Li YJ, Wu BL, et al. A patient with COVID-19 presenting a false-negative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction result. Korean J Radiol 2020; 21(5):623-4. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2020.0195.
doi: 10.3348/kjr.2020.0195 pmid: 32207257 |
| 9. | Liu K, Li Q, Ma JC, et al. Evaluating a fully automated pulmonary nodule detection approach and its impact on radiologist performance. Radiology: Artificial Intellig 2019; 1(3):e180084. doi: 10.1148/ryai.2019180084. |
| 10. |
Huang L, Han R, Ai T, et al. Serial quantitative chest CT assessment of COVID-19: a deep learning approach. Radiology: Cardiothoracic Imaging 2020; 2(2):e200075. doi: 10.1148/ryct.2020200075.
doi: 10.1148/ryct.2020200075 pmid: 33778562 |
| 11. |
Wang Y, Yan FR, Lu XF, et al. IILS: Intelligent imaging layout system for automatic imaging report standardization and intra-interdisciplinary clinical workflow optimization. EBioMedicine 2019; 44:162-81. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.05.040.
doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.05.040 pmid: 31129095 |
| 12. |
Wang MH, Xia C, Huang L, et al. Deep learning-based triage and analysis of lesion burden for COVID-19: a retrospective study with external validation. Lancet Digit Health 2020; 2(10):e506-e515. doi: 10.1016/S2589-7500(20)30199-0.
doi: 10.1016/S2589-7500(20)30199-0 pmid: 32984796 |
| [1] | Changyi Liu, Xiaoqing Liu, Xiaochun Shi. Clinical Features of Spontaneous Remission in the Classic Fever of Unknown Origin: A Retrospective Study [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2022, 37(2): 134-141. |
| [2] | Huizi Gong, Mengyin Wu, Jun Li, Heyi Zheng. The Great Imitator: Atypical Cutaneous Manifestations of Primary Syphilitic Chancre [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(4): 279-283. |
| [3] | Pengfei Qu, Baoliang Bai, Ting Duan, Kai Liu, Jinliang Du, Xin Xiong, Penglin Jia, Zhongchun Sun, Puping Lei. Pneumonia, Multiple Pulmonary Infarction and Abscess Caused by a Bamboo Stick Accidentally Piercing into Chest: a Case Misdiagnosed as Pulmonary Tuberculosis [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(3): 252-256. |
| [4] | Wei Ba, Shuhao Wang, Cancheng Liu, Yuefeng Wang, Huaiyin Shi, Zhigang Song. Histopathological Diagnosis System for Gastritis Using Deep Learning Algorithm [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(3): 204-209. |
| [5] | Lianyan Xu, Ke Yan, Le Lu, Weihong Zhang, Xu Chen, Xiaofei Huo, Jingjing Lu. External and Internal Validation of a Computer Assisted Diagnostic Model for Detecting Multi-Organ Mass Lesions in CT images [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(3): 210-217. |
| [6] | Jiazheng Li, Lei Tang. Radiomics in Antineoplastic Agents Development: Application and Challenge in Response Evaluation [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(3): 187-195. |
| [7] | Bin Wu,Jianghua Zhou,Wenxin Wang,Huilin Yang,Meng Xia,Binghong Zhang,Zhigang She,Hongliang Li. Association Analysis of Hyperlipidemia with the 28-Day All-Cause Mortality of COVID-19 in Hospitalized Patients [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(1): 17-26. |
| [8] | Jian Cao, Guorong Wang, Zhiwei Wang, Zhengyu Jin. CT Texture Analysis: A Potential Biomarker for Evaluating KRAS Mutational Status in Colorectal Cancer [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(4): 306-314. |
| [9] | Wang Xiaolei, Meng Shanshan, Duan Kehang, Hu Yaowei, Wei Feng. Treatment of Retroperitoneal Cavernous Lymphangioma: A Case Report [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(3): 283-285. |
| [10] | Wu Ziquan, Zeng Delu, Yao Jiangling, Bian Yangyang, Gu Yuntao, Meng Zhulong, Fu Jian, Peng Lei. Research Progress on Diagnosis and Treatment of Chronic Osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(3): 211-220. |
| [11] | Li Peilin, Yuan Zhenming, Tu Wenbo, Yu Kai, Lu Dongxin. Medical Knowledge Extraction and Analysis from Electronic Medical Records Using Deep Learning [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(2): 133-139. |
| [12] | Shi Ying-huan,Wang Qian. The Artificial Intelligence-Enabled Medical Imaging: Today and Its Future [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(2): 71-75. |
| [13] | Wang Yingwei, Zhang Xinghua, Wang Botao, Wang Ye, Liu Mengqi, Wang Haiyi, Ye Huiyi, Chen Zhiye. Value of Texture Analysis of Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Parameters in Differential Diagnosis of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor and Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 1-9. |
| [14] | Wang Botao, Liu Mingxia, Chen Zhiye. Differential Diagnostic Value of Texture Feature Analysis of Magnetic Resonance T2 Weighted Imaging between Glioblastoma and Primary Central Neural System Lymphoma [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 10-17. |
| [15] | Wang Botao, Fan Wenping, Xu Huan, Li Lihui, Zhang Xiaohuan, Wang Kun, Liu Mengqi, You Junhao, Chen Zhiye. Value of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Texture Analysis in the Differential Diagnosis of Benign and Malignant Breast Tumors [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 33-37. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|

