Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2020, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (4): 306-314.doi: 10.24920/003770
• Original Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
CT Texture Analysis: A Potential Biomarker for Evaluating KRAS Mutational Status in Colorectal Cancer
Jian Cao, Guorong Wang, Zhiwei Wang( ), Zhengyu Jin
), Zhengyu Jin
- Department of Radiology, Peking Union Medical College Hospital,Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100730, China
-
Received:2020-04-30Accepted:2020-07-16Published:2020-12-31Online:2021-01-08 -
Contact:Zhiwei Wang E-mail:zhiweiwang1981@sina.com
Cite this article
Jian Cao, Guorong Wang, Zhiwei Wang, Zhengyu Jin. CT Texture Analysis: A Potential Biomarker for Evaluating KRAS Mutational Status in Colorectal Cancer[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(4): 306-314.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Table 1
Comparision of Clinical characteristics of the CRC patients between KRAS mutated group and KRAS wild-type group in the training cohort and validation cohort§"
| Characteristics | Training cohort | Validation cohort | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mutated group (n=27) | Wild-type group (n=24) | t/x2 | P | Mutated group (n=25) | Wild-type group (n=16) | t/x2 | P | ||
| Age (years) | 61.1±10.4 | 59.4±13.9 | 0.258 | 0.620 | 58.0±14.4 | 59.9±9.8 | 0.223 | 0.610 | |
| Gender [n (%)] | 1.457 | 0.227 | 0.009 | 0.923 | |||||
| Male | 9 (33.3) | 12 (50.0) | 9 (36.0) | 6 (37.5) | |||||
| Female | 18 (66.7) | 12 (50.0) | 16 (64.0) | 10 (62.5) | |||||
| Tumor location [n (%)] | 0.695 | 0.952 | 9.163 | 0.057 | |||||
| Ascending colon | 8 (29.6) | 7 (29.2) | 10 (40.0) | 1 (6.3) | |||||
| Transverse colon | 2 (7.4) | 1 (4.2) | 0 (0) | 1 (6.3) | |||||
| Descending colon | 2 (7.4) | 1 (4.2) | 0 (0) | 2 (12.5) | |||||
| Sigmoid colon | 6 (22.2) | 7 (29.2) | 5 (20.0) | 4 (25.0) | |||||
| Rectum | 9 (33.3) | 8 33.3) | 10 (40.0) | 8 (50.0) | |||||
| Tumor size (mm) | 14.6±3.3 | 15.2±3.8 | 0.357 | 0.553 | 15.4±3.9 | 14.2±3.4 | 0.898 | 0.349 | |
| Histological grade [n (%)] | 1.153 | 0.562 | 0.391 | 0.822 | |||||
| Well | 8 (29.6) | 5 (20.8) | 3 (12.0) | 2 (12.5) | |||||
| Moderate | 14 (51.9) | 16 (66.7) | 17 (68.0) | 12 (75.0) | |||||
| Poor | 5 (18.5) | 3 (12.5) | 5 (20.0) | 2 (12.5) | |||||
| T stage [n (%)] | 1.979 | 0.372 | 1.128 | 0.288 | |||||
| T1 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | |||||
| T2 | 4 (14.8) | 1 (4.2) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | |||||
| T3 | 12 (44.4) | 10 (41.7) | 13 (52.0) | 11 (68.8) | |||||
| T4 | 11 (40.7) | 13 (54.2) | 12 (48.0) | 5 (31.3) | |||||
| N stage [n (%)] | 2.204 | 0.332 | 2.046 | 0.360 | |||||
| N0 | 8 (29.6) | 3 (12.5) | 9 (36.0) | 4 (25.0) | |||||
| N1 | 9 (33.3) | 10 (41.7) | 10 (40.0) | 10 (62.5) | |||||
| N2 | 10 (37.0) | 11 (45.8) | 6 (24.0) | 2 (12.5) | |||||
| M stage [n (%)] | 2.422 | 0.120 | 0.010 | 0.922 | |||||
| M0 | 4 (14.8) | 8 (33.3) | 5 (20.0) | 3 (18.8) | |||||
| M1 | 23 (85.2) | 16 (66.7) | 20 (80.0) | 13 (81.3) | |||||
Table 2
Diagnostic efficiencies of the models and incorporated features from the unenhanced and contrast-enhanced CT images"
| Models | CT images | Selected features | Training cohort (n=51) | Validation cohort (n=41) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC (95% CI) | Cut-off value | Sen (%) | Spe (%) | AUC (95% CI) | Cut-off value | Sen (%) | Spe (%) | ||||
| Model 1 | CE | entropy (CT_SSF 2) | 0.951 (0.895-1) | 4.11* | 91.7 | 88.9 | 0.951 (0.891-1) | 4.06* | 100 | 84 | |
| Model 2 | Non-CE | skewness (CT_SSF 5) | 0.951 (0.895-1) | 0.46# | 88.9 | 91.7 | 0.995 (0.982-1) | 0.28# | 100 | 93.7 | |
| CE | skewness (CT_SSF 0) | ||||||||||
| CE | entropy (CT_SSF 2) | ||||||||||
| CE | kurtosis (CT_SSF 0) | ||||||||||
| CE | kurtosis (CT_SSF 3) | ||||||||||
| CE | mean (CT_SSF 3) | ||||||||||

Figure 1.
CT image and texture images of descending colon cancer without KRAS mutation (female, 54-year-old, T4N1M1, histological grade: moderate). (A) The unenhanced CT image; (B), (C), (D) are the corresponding texture images at scale of fine, medium, coarse; (E) the contrast-enhanced CT image; (F), (G), (H) are the corresponding texture images at scale of fine, medium, coarse (The blue circles are the ROI where texture analyses were performed)."
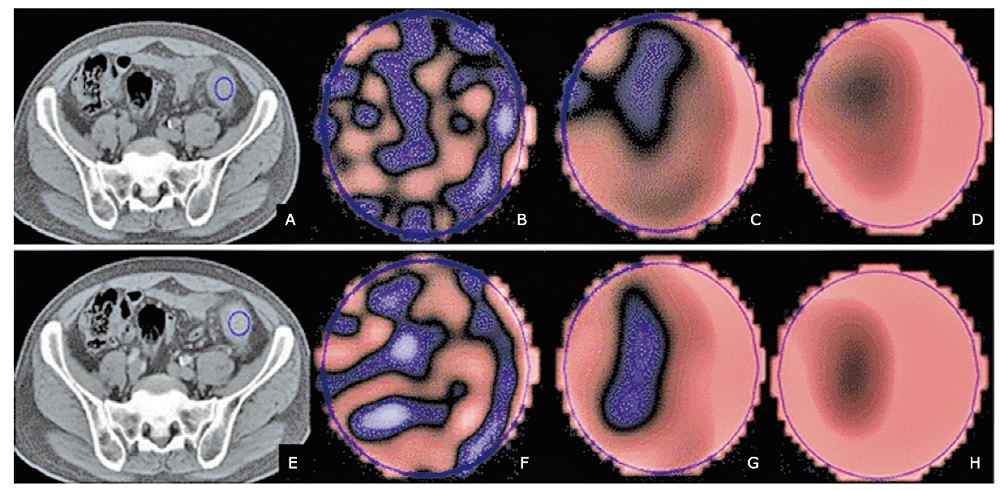

Figure 2.
CT image and texture images of rectal cancer with KRAS mutation (male, 58-year-old, T3N1M1, histological grade: moderate). (A) The unenhanced CT image; (B),(C),(D) are the corresponding texture images at scale of fine, medium, coarse; (E) the contrast-enhanced CT image; (F), (G), (H) are the corresponding texture images at scale of fine, medium, coarse (The blue circles are the ROI where texture analyses were performed)."
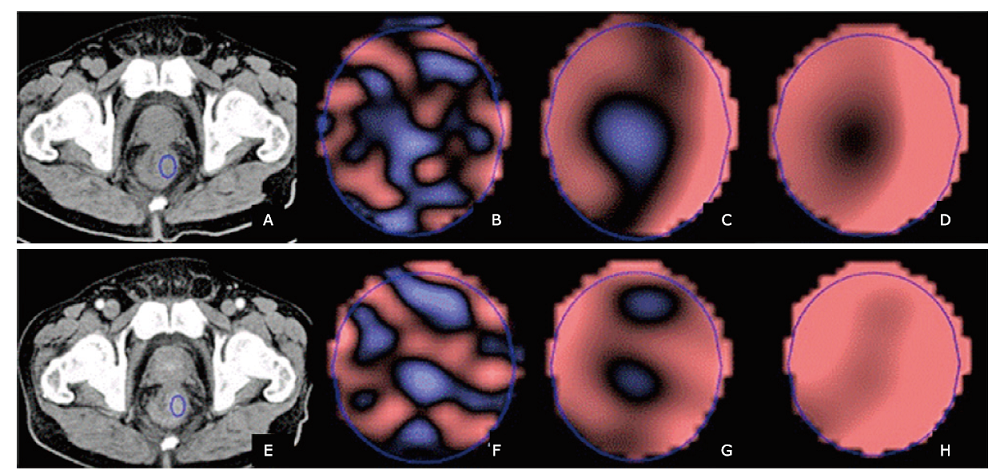
Table 3
Diagnostic efficiencies of the models and incorporated features from unenhanced or contrast-enhanced CT images alone"
| Models | CT images | Selected features | Training cohort | Validation cohort | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC (95% CI) | Cut-off value | Sen (%) | Spe (%) | AUC (95% CI) | Cut-off value | Sen (%) | Spe (%) | ||||
| Model 3 | Non-CE | MPP (CT_SSF 0) entropy (CT_SSF 2) skewness (CT_SSF 3) kurtosis (CT_SSF 5) | 0.975 (0.939-1) | 0.39* | 96.3 | 91.7 | 0.963 (0.907-1) | 0.79* | 88.0 | 93.7 | |
| Model 4 | CE | kurtosis (CT_SSF 0) entropy (CT_SSF 2) kurtosis (CT_SSF 3) skewness (CT_SSF 4) | 0.951 (0.895-1) | 0.46* | 88.9 | 91.7 | 0.951 (0.891-1) | 0.80* | 84.0 | 100 | |
| 1. |
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2018; 68(6):394-424. doi: 10.3322/caac.21492.
doi: 10.3322/caac.21492 pmid: 30207593 |
| 2. |
Freeman HJ. Heterogeneity of colorectal adenomas, the serrated adenoma, and implications for screening and surveillance. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(22):3461-3. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.3461.
doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.3461 pmid: 18567071 |
| 3. | Yu GZ, Chen Y, Long YQ, et al. New insight into the key proteins and pathways involved in the metastasis of colorectal carcinoma. Oncol reports 2008; 19(5):1191-204. doi: 10.3892/or.19.5.1191. |
| 4. |
Labianca R, Nordlinger B, Beretta GD, et al. Primary colon cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, adjuvant treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 2010; 21(Suppl 5):v70-7. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdq168.
doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdq168 |
| 5. |
Ulivi P, Capelli L, Valgiusti M, et al. Predictive role of multiple gene alterations in response to cetuximab in metastatic colorectal cancer: a single center study. J Translation Med 2012; 10:87. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-10-87.
doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-10-87 |
| 6. |
Berger MD, Stintzing S, Heinemann V, et al. Impact of genetic variations in the MAPK signaling pathway on outcome in metastatic colorectal cancer patients treated with first-line FOLFIRI and bevacizumab: data from FIRE-3 and TRIBE trials. Ann Oncol 2017; 28(11):2780-85. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx412.
pmid: 29045529 |
| 7. | Baselga J. The EGFR as a target for anticancer therapy:focus on cetuximab. Eur J Cancer 2001; 37(Suppl 4):S16-22. doi: 10.1016/s0959-8049(01)00233-7. |
| 8. |
Napolitano S, Martini G, Martinelli E, et al. Therapeutic efficacy of SYM004, a mixture of two anti-EGFR antibodies in human colorectal cancer with acquired resistance to cetuximab and MET activation. Oncotarget 2017; 8(40):67592-604. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.18749.
doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.18749 pmid: 28978055 |
| 9. |
Cremolini C, Schirripa M, Antoniotti C, et al. First-line chemotherapy for mCRC-a review and evidence-based algorithm. Nature Reviews Clin Oncol 2015; 12(10):607-19. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2015.129.
doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2015.129 |
| 10. |
Michl M, Stintzing S, Fischer von Weikersthal L, et al. CEA response is associated with tumor response and survival in patients with KRAS exon 2 wild-type and extended RAS wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer receiving first-line FOLFIRI plus cetuximab or bevacizumab (FIRE-3 trial). Ann Oncol 2016; 27(8):1565-72. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdw222.
pmid: 27234640 |
| 11. |
Tsujikawa T, Yamamoto M, Shono K, et al. Assessment of intratumor heterogeneity in mesenchymal uterine tumor by an (18)F-FDG PET/CT texture analysis. Ann Nucl Med 2017; 31(10):752-57. doi: 10.1007/s12149-017-1208-x.
pmid: 28905201 |
| 12. | Zhang GM, Shi B, Sun H, et al. Differentiating pheochromocytoma from lipid-poor adrenocortical adenoma by CT texture analysis: feasibility study. Abd Radiol 2017; 42(9):2305-13. doi: 10.1007/s00261-017-1118-3. |
| 13. |
Liu S, Zheng H, Pan X, et al. Texture analysis of CT imaging for assessment of esophageal squamous cancer aggressiveness. J Thorac Dis 2017; 9(11):4724-32. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2017.06.46.
pmid: 29268543 |
| 14. |
Liu Y, Liu S, Qu F, et al. Tumor heterogeneity assessed by texture analysis on contrast-enhanced CT in lung adenocarcinoma: association with pathologic grade. Oncotarget 2017; 8(32):53664-74. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15399.
doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15399 pmid: 28881840 |
| 15. |
Kim HS, Kim JH, Yoon YC, et al. Tumor spatial heterogeneity in myxoid-containing soft tissue using texture analysis of diffusion-weighted MRI. PLoS One 2017; 12(7):e0181339. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0181339.
pmid: 28708850 |
| 16. |
Craigie M, Squires J, Miles K. Can CT measures of tumour heterogeneity stratify risk for nodal metastasis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer? Clin Radiol 2017; 72(10):899.e1-9899.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2017.04.013.
doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2017.04.013 |
| 17. |
Miles KA, Ganeshan B, Rodriguez-Justo M, et al. Multifunctional imaging signature for V-KI-RAS2 Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog (KRAS) mutations in colorectal cancer. J Nucl Med 2014; 55(3):386-91. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.113.120485.
doi: 10.2967/jnumed.113.120485 |
| 18. |
Ukweh ON, Ugbem TI, Okeke CM, et al. Value and diagnostic efficacy of fetal morphology assessment using ultrasound in a poor-resource setting. Diagnost 2019; 9(3):109. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics9030109.
doi: 10.3390/diagnostics9030109 |
| 19. |
Feng C, Lu F, Shen Y, et al. Tumor heterogeneity in gastrointestinal stromal tumors of the small bowel: volumetric CT texture analysis as a potential biomarker for risk stratification. Cancer imaging 2018; 18(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s40644-018-0182-4.
doi: 10.1186/s40644-018-0182-4 pmid: 30518436 |
| 20. |
Lubner MG, Smith AD, Sandrasegaran K, et al. CT texture analysis: definitions, applications, biologic correlates, and challenges. Radiographics 2017; 37(5):1483-503. doi: 10.1148/rg.2017170056.
doi: 10.1148/rg.2017170056 pmid: 28898189 |
| 21. |
Weiss GJ, Ganeshan B, Miles KA, et al. Noninvasive image texture analysis differentiates K-ras mutation from pan-wildtype NSCLC and is prognostic. PLoS One 2014; 9(7):e100244. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0100244.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0100244 pmid: 24987838 |
| 22. |
Ba-Ssalamah A, Muin D, Schernthaner R, et al. Texture-based classification of different gastric tumors at contrast-enhanced CT. Eur J Radiol 2013; 82(10):e537-43. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2013.06.024.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2013.06.024 |
| 23. | Lubner MG, Stabo N, Lubner SJ, et al. CT textural analysis of hepatic metastatic colorectal cancer: pre-treatment tumor heterogeneity correlates with pathology and clinical outcomes. Abd Imaging 2015; 40(7):2331-7. doi: 10.1007/s00261-015-0438-4. |
| 24. |
Beckers RCJ, Trebeschi S, Maas M, et al. CT texture analysis in colorectal liver metastases and the surrounding liver parenchyma and its potential as an imaging biomarker of disease aggressiveness, response and survival. Eur J Radiol 2018; 102:15-21. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2018.02.031.
pmid: 29685529 |
| 25. |
Lee SJ, Zea R, Kim DH, et al. CT texture features of liver parenchyma for predicting development of metastatic disease and overall survival in patients with colorectal cancer. Eur Radiol 2018; 28(4):1520-28. doi: 10.1007/s00330-017-5111-6.
doi: 10.1007/s00330-017-5111-6 pmid: 29164382 |
| 26. |
Chee CG, Kim YH, Lee KH, et al. CT texture analysis in patients with locally advanced rectal cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy: A potential imaging biomarker for treatment response and prognosis. PLoS One 2017; 12(8):e0182883. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0182883.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0182883 pmid: 28797063 |
| 27. |
Lovinfosse P, Koopmansch B, Lambert F, et al. (18)F-FDG PET/CT imaging in rectal cancer: relationship with the RAS mutational status. Br J Radiol 2016; 89(1063):20160212. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20160212.
doi: 10.1259/bjr.20160212 pmid: 27146067 |
| 28. |
Miles KA, Ganeshan B, Rodriguez-Justo M, et al. Multifunctional imaging signature for V-KI-RAS2 Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog (KRAS) mutations in colorectal cancer. J Nucl Med 2014; 55(3):386-91. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.113.120485.
doi: 10.2967/jnumed.113.120485 pmid: 24516257 |
| 29. |
Chen SW, Chiang HC, Chen WT, et al. Correlation between PET/CT parameters and KRAS expression in colorectal cancer. Clin Nucl Med 2014; 39(8):685-9. doi: 10.1097/rlu.0000000000000481.
pmid: 24978328 |
| 30. |
Kawada K, Nakamoto Y, Kawada M, et al. Relationship between 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose accumulation and KRAS/BRAF mutations in colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2012; 18(6):1696-703. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-11-1909.
pmid: 22282467 |
| 31. |
Kawada K, Toda K, Nakamoto Y, et al. Relationship between 18F-FDG PET/CT scans and KRAS mutations in metastatic colorectal cancer. J Nucl Med 2015; 56(9):1322-7. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.115.160614.
doi: 10.2967/jnumed.115.160614 pmid: 26135109 |
| 32. |
Yang L, Dong D, Fang M, et al. Can CT-based radiomics signature predict KRAS/NRAS/BRAF mutations in colorectal cancer? Eur Radiol 2018; 28(5):2058-67. doi: 10.1007/s00330-017-5146-8.
doi: 10.1007/s00330-017-5146-8 pmid: 29335867 |
| [1] | Dasheng Li,Dawei Wang,Nana Wang,Haiwang Xu,He Huang,Jianping Dong,Chen Xia. An Insight of the First Community Infected COVID-19 Patient in Beijing by Imported Case: Role of Deep Learning-Assisted CT Diagnosis [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(1): 66-71. |
| [2] | Wang Yingwei, Zhang Xinghua, Wang Botao, Wang Ye, Liu Mengqi, Wang Haiyi, Ye Huiyi, Chen Zhiye. Value of Texture Analysis of Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Parameters in Differential Diagnosis of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor and Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 1-9. |
| [3] | Wang Botao, Liu Mingxia, Chen Zhiye. Differential Diagnostic Value of Texture Feature Analysis of Magnetic Resonance T2 Weighted Imaging between Glioblastoma and Primary Central Neural System Lymphoma [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 10-17. |
| [4] | Liu Hongjuan, Zhou Huanfen, Zong Linxiong, Liu Mengqi, Wei Shihui, Chen Zhiye. MRI Histogram Texture Feature Analysis of the Optic Nerve in the Patients with Optic Neuritis [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 18-23. |
| [5] | Xu Jia, Wang Xuan, Jin Zhengyu, You Yan, Wang Qin, Wang Shitian, Xue Huadan. Value of Texture Analysis on Gadoxetic Acid-enhanced MR for Detecting Liver Fibrosis in a Rat Model [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 24-32. |
| [6] | Wang Botao, Fan Wenping, Xu Huan, Li Lihui, Zhang Xiaohuan, Wang Kun, Liu Mengqi, You Junhao, Chen Zhiye. Value of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Texture Analysis in the Differential Diagnosis of Benign and Malignant Breast Tumors [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 33-37. |
| [7] | Wang Guorong, Wang Zhiwei, Jin Zhengyu. Application and Progress of Texture Analysis in the Therapeutic Effect Prediction and Prognosis of Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy for Colorectal Cancer [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 45-50. |
| [8] | Li Ping, Zhu Liang, Wang Xuan, Xue Huadan, Wu Xin, Jin Zhengyu. Imaging Diagnosis of Type Ⅲ Choledochal Cyst: A Case Report [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(3): 194-203. |
| [9] | Li Tao, Yang Li, Zhang Weiguo, Luo Chuncai, Huang Zili, Li Jinfeng, Li Xin. Midterm Follow-up of Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting with 64-Slice Multi-detector Computed Tomography: Identification of Risk Factors Affecting Graft Patency [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(2): 69-76. |
| [10] | Wang Ting, Ma Lin, Lou Xin, Bu Bo. Trigeminal Ganglioneuroma in the Middle-posterior Cranial Fossa: a Case Report△ [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2017, 32(2): 123-128. |
| [11] | Li Tao, Zhao Shaohong, Li Jinfeng, Huang Zili, Luo Chuncai, Yang Li. Value of Multi-detector CT in Detection of Isolated Spontaneous Superior Mesenteric Artery Dissection [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2017, 32(1): 28-33. |
| [12] | Chen Xing, Wang Lihua, Zhang Lixian, Zhao Caihong. IgG4-related Autoimmune Pancreatitis Mimicking Acute Pancreatitis: A Case Report [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2017, 32(1): 65-68. |
| [13] | Yu Wang, Zi-yuan Liu, Wan-chen Dou, Wen-bin Ma, Ren-zhi Wang, Yi Guo. Application of Preoperative CT/MRI Image Fusion in Target Positioning for Deep Brain Stimulation [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2016, 31(3): 161-167. |
| [14] | Da-ming Zhang, Xuan Wang, Hua-dan Xue, Zheng-yu Jin*, Hao Sun, Yu Chen, Yong-lan He. Determinants of Detection of Stones and Calcifications in the Hepatobiliary System on Virtual Nonenhanced Dual-energy CT [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2016, 31(2): 76-82. |
| [15] | Zhi-wei Wang, Hua-dan Xue, Xiao-guang Li, Jie Pan, Xiao-bo Zhang, Zheng-yu Jin. Life-threatening Spontaneous Retroperitoneal Haemorrhage: Role of Multidetector CT-angiography for the Emergency Management [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2016, 31(1): 43-48. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|

