Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2020, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (2): 142-150.doi: 10.24920/003643
应用T1加权超微小氧化铁纳米颗粒进行早期肝癌靶向磁共振成像的体内外研究
- 上海交通大学附属第一人民医院 放射科,上海 200080,中国
-
收稿日期:2019-07-26接受日期:2019-12-10出版日期:2020-06-30发布日期:2020-06-09 -
通讯作者:王悍 E-mail:13564112852@163.com
Targeted MR Imaging Adopting T1-Weighted Ultra-Small Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Early Hepatocellular Carcinoma: An in vitro and in vivo Study
Xu Yanhong,Yang Jia,Meng Jie,Wang Han( )
)
- Department of Radiology, Shanghai General Hospital, Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200080, China
-
Received:2019-07-26Accepted:2019-12-10Published:2020-06-30Online:2020-06-09 -
Contact:Wang Han E-mail:13564112852@163.com
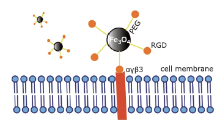
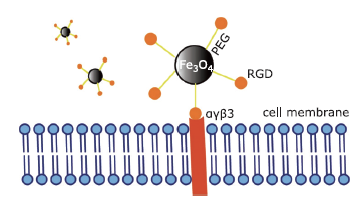
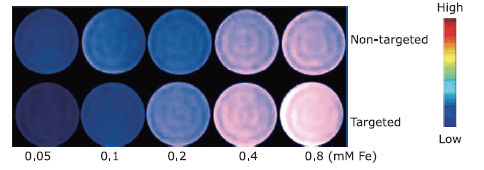
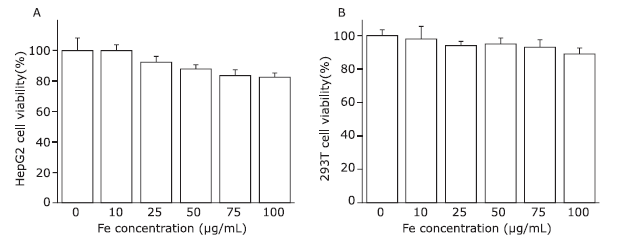
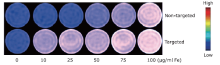
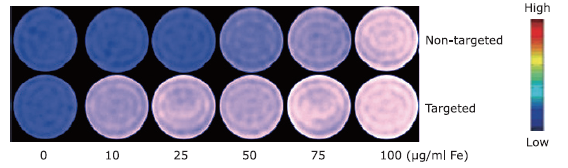
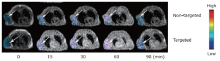
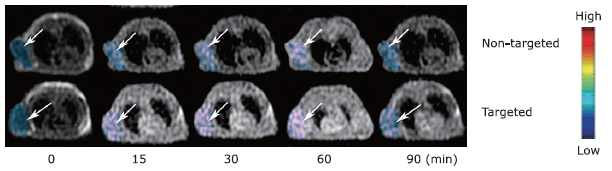
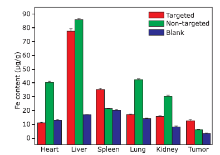
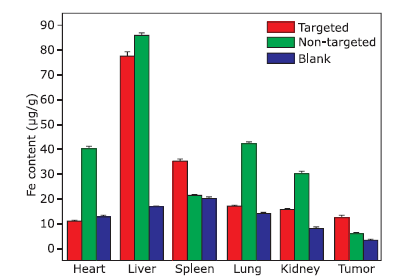
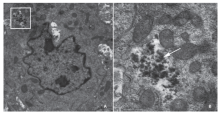
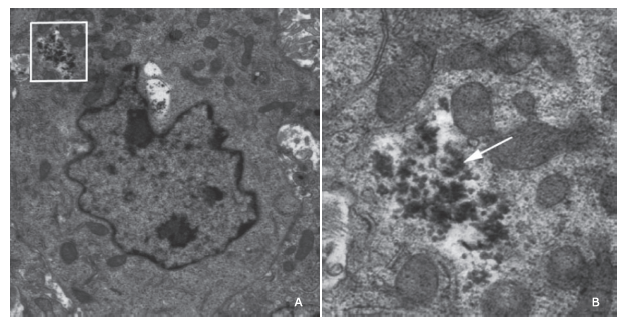
摘要: 目的 制备精氨酰甘氨酸天冬氨酸肽(RGD)修饰的超小型超顺磁性氧化铁(Fe3O4)纳米粒(NPs),用于肝细胞癌(HCC)细胞的靶向磁共振(MR)成像,并通过体外和体内实验验证其作为T1阳性磁共振成像对比剂的应用价值。方法 将柠檬酸钠稳定的羧化Fe3O4 NPs与聚乙二醇(PEG)连接的RGD纳米粒子(NPs)偶联,形成靶向造影剂Fe3O4-PEG-RGD。通过HepG2细胞摄取和细胞MR成像,研究Fe3O4-PEG-RGD与RGD受体结合的特异性,并通过对裸鼠皮下HepG2肿瘤的体内MR成像,研究Fe3O4-PEG-RGD与RGD受体结合的特异性。结果 合成的Fe3O4-PEG-RGD纳米颗粒具有良好的生物相容性和超高的r1弛豫率(1.37 mM -1S -1),Fe3O4-PEG-RGD纳米颗粒的形貌均为球形,平均直径约2.7 nm。体外细胞摄取和细胞磁共振成像证实了其对HepG2细胞的靶向作用。同时,Fe3O4-PEG-RGD对小鼠肿瘤MR信号的增强作用明显高于非靶向Fe3O4-RGD。 结果 Fe3O4-PEG-RGD颗粒在肝细胞癌靶向MR成像中作为T1阳性造影剂具有潜在的应用价值。
引用本文
Xu Yanhong,Yang Jia,Meng Jie,Wang Han. Targeted MR Imaging Adopting T1-Weighted Ultra-Small Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Early Hepatocellular Carcinoma: An in vitro and in vivo Study[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(2): 142-150.
| 1 |
1. Kavanaugh G, Williams J, Morris AS , et al. Utility of [18F] FSPG PET to image hepatocellular carcinoma: first clinical evaluation in a US population. Mol Imaging Biol 2016; 18(6):924-34. doi: 10.1007/s11307-016-1007-0.
doi: 10.1007/s11307-016-1007-0 pmid: 27677886 |
| 2. |
Bruix J, Sherman M . Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2014; 10(5):761-80. doi: 10.1016/j.gassur.2005.10.006.
doi: 10.1002/hep.1840100502 pmid: 2680866 |
| 3. |
Chalasani N, Said A, Ness R , et al. Screening for hepatocellular carcinoma in patient with cirrhosis in the United States: results of a national survey. Am J Gastroenterol 1999; 94(8):2224-9. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9270(99)00353-6.
doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.1999.01297.x pmid: 10445554 |
| 4. |
Yamamoto M, Takasaki K, Otsubo T , et al. Favorable surgical outcomes in patients with early hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg 2004; 239(3):395-9. doi: 10.1097/01.sla.0000114215.03112.e0.
doi: 10.1097/01.sla.0000114215.03112.e0 pmid: 15075658 |
| 5. |
Liu H, Xu Y, Wen S , et al. Targeted tumor computed tomography imaging using low-generation dendrimer-stabilized gold nanoparticles. Chemistry 2013; 19(20):6409-16. doi: 10.1002/chem.201204612.
doi: 10.1002/chem.201204612 pmid: 23505030 |
| 6. |
Lim JH, Kim CK, Lee WJ , et al. Detection of hepatocellular carcinomas and dysplastic nodules in cirrhotic livers: accuracy of helical CT in transplant patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2000; 175(3):693-8. doi: 10.2214/ajr.175.3.1750693.
doi: 10.2214/ajr.175.3.1750693 pmid: 10954452 |
| 7. |
Semelka RC, Martin DR, Balci C , et al. Focal liver lesions: comparison of dual-phase CT and multisequence multiplanar MR imaging including dynamic gadolinium enhancement. J Magn Reson Imaging 2001; 13(3):397-401. doi: 10.1002/jmri.1057.
doi: 10.1002/jmri.1057 pmid: 11241813 |
| 8. |
Tsekouras, Magkos YE, Kellas F, , et al. High-intensity interval aerobic training reduces hepatic very low-density lipoprotein-triglyceride secretion rate in men. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2008; 295(4):E851. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.90545.2008.
doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.90545.2008 pmid: 18664593 |
| 9. | Nobuhiro F, Akihiro N, Yoshiki A , et al. Significance of the signal intensity of gadoxetic acid-enhanced MR imaging for predicting the efficacy of hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Magnet Reson Med Sci 2016; 15(1):111-20. doi: 10.2463/mrms.2015-0012. |
| 10. |
Gan LU, Chang R, Jin H , et al. Typical CT and MRI signs of hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma. Oncology Letters 2016; 11(3):1699-706. doi: 10.3892/ol.2016.4149.
doi: 10.3892/ol.2016.4149 pmid: 26998064 |
| 11. |
Kim SA, Lee JM, Lee KB , et al. Intrahepatic massforming cholangiocarcinomas: enhancement patterns at multiphasic CT, with special emphasis on arterial enhancement pattern-correlation with clinicopathologic findings. Radiology 2011; 260(1):148-57. doi: 10.1148/radiol.11101777.
doi: 10.1148/radiol.11101777 |
| 12. |
Forner A, Vilana R, Ayuso C , et al. Diagnosis of hepatic nodules 20 mm or smaller in cirrhosis: prospective validation of the noninvasive diagnostic criteria for hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2008; 47(6):97-104. doi: 10.1002/hep.22356.
doi: 10.1002/hep.21966 |
| 13. |
Kim I, Kim MJ . Histologic characteristics of hepatocellular carcinomas showing atypical enhancement patterns on 4-phase MDCT examination. Korean J Radiol 2012; 13(5):586-93. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2012.13.5.586.
doi: 10.3348/kjr.2012.13.5.586 |
| 14. |
Xu Y, Xiao A, Yang J , et al. Assessment of lipiodol deposition and residual cancer for hepatocellular carcinoma after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization via iodine-based material decomposition images with spectral computed tomography imaging: a preliminary study. Iran J Radiol 2015; 12(4):e26009. doi: 10.5812/iranjradiol.26009.
doi: 10.5812/iranjradiol.26009 pmid: 26715981 |
| 15. |
Khan AS, Hussain HK, Johnson TD , et al. Value of delayed hypointensity and delayed enhancing rim in magnetic resonance imaging diagnosis of small hepatocellular carcinoma in the cirrhotic liver. J Magn Reson Imaging 2010; 32(2):360-6. doi: 10.1002/jmri.22271.
doi: 10.1002/jmri.22271 pmid: 20677263 |
| 16. |
Jia C, Dai C, Zhao X , et al. Use of hepatic blood inflow occlusion and hemihepatic artery retention in liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. Translation Cancer Res 2016; 5(5):598-606. doi: 10.21037/tcr.2016.10.50.
doi: 10.21037/tcr |
| 17. |
Wayne LW . Regulatory processes interacting to maintain hepatic blood flow constancy: Vascular compliance, hepatic arterial buffer response, hepatorenal reflex, liver regeneration, escape from vasoconstriction. Hepatology Res 2010; 37(11):891-903. doi: 10.1111/j.1872-034X.2007.00148.x.
doi: 10.1111/hep.2007.37.issue-11 |
| 18. |
Vanagas T, Gulbinas A, Pundzius J , et al. Radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors (II): clinical application and outcomes. Medicina 2010; 46(1):81-8. doi: 10.1159/000320314.
doi: 10.3390/medicina46020012 |
| 19. |
Pysz MA, Gambhir SS, Willmann JK . Molecular imaging: current status and emerging strategies. Clin Radiol 2010; 65(7):500-16. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2010.03.011.
doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2010.03.011 |
| 20. |
Mundt AP, Winter C, Mueller S , et al. Targeting activated microglia in Alzheimer’s pathology by intraventricular delivery of a phagocytosable MR imaging contrast agent in APP23 transgenic mice. Neuroimage 2009; 46(2):367-72. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.01.067.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.01.067 |
| 21. |
Oude Engberink RD, van der Pol SM, Dopp EA , et al. Comparison of SPIO and USPIO for in vitro labeling of human monocytes: MR detection and cell function. Radiology 2007; 243(2):467-74. doi: 10.1124/jpet.105.100149.
doi: 10.1148/radiol.2432060120 pmid: 17456871 |
| 22. |
Xu Y, Yang J, Zhang Z , et al. MRI for discriminating metastatic ovarian tumors from primary epithelial ovarian cancers. J Ovarian Res 2015; 8:61. doi: 10.1186/s13048-015-0188-5.
doi: 10.1186/s13048-015-0188-5 pmid: 26310488 |
| 23. |
Stoll G, Bendszus M, Perez J , et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of the peripheral nervous system. J Neurol 2009; 256(7):1043-51. doi: 10.1007/s00415-009-5064-z.
doi: 10.1007/s00415-009-5064-z |
| 24. |
Anderson SA, Shukaliak-Quandt J, Jordan EK , et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of labeled T-cells in a mouse model of multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 2004; 55(5):654-9. doi: 10.1002/ana.20066.
doi: 10.1002/ana.20066 pmid: 15122705 |
| 25. |
Patterson AJ, Tang TY, Graves MJ , et al. In vivo carotid plaque MRI using quantitative T2* measurements with ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide particles: a dose-response study to statin therapy. NMR Biomed 2011; 24(1):89-95. doi: 10.1002/nbm.1560.
doi: 10.1002/nbm.1560 pmid: 21259368 |
| 26. |
Yang J, Wadghiri YZ, Hoang DM , et al. Detection of amyloid plaques targeted by USPIO-Abeta1-42 in Alzheimer’s disease transgenic mice using magnetic resonance microimaging. Neuroimage 2011; 55(4):1600-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.01.023.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.01.023 pmid: 21255656 |
| 27. |
Liu H, Wang H, Xu Y , et al. Lactobionic acid-modified dendrimer-entrapped gold nanoparticles for targeted computed tomography imaging of human hepatocellular carcinoma. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2014; 6(9):6944-53. doi: 10.1021/am500761x.
doi: 10.1021/am500761x pmid: 24712914 |
| 28 |
28. Zhai C, Franssen GM, Petrik M , et al. Comparison of Ga-68-Labeled Fusarinine C-Based multivalent RGD conjugates and [(68)Ga]NODAGA-RGD-in vivo imaging studies in human xenograft tumors. Mol Imaging Biol 2016; 18(5):758-67. doi: 10.1007/s11307-016-0931-3.
doi: 10.1007/s11307-016-0931-3 pmid: 26905697 |
| 29. |
Chen PJ, Hu SH, Hsiao CS , et al. Multifunctional magnetically removable nanogated lids of Fe3O4-capped mesoporous silica nanoparticles for intracellular controlled release and MR imaging. J Mater Chem 2011; 21(8):2535-43. doi: 10.1039/c0jm02590a.
doi: 10.1039/c0jm02590a |
| 30. |
Xie J, Chen K, Lee HY , et al. Ultrasmall c (RGDyK)-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles and their specific targeting to integrin αvβ3-rich tumor cells. J Am Chem Soc 2011; 130(24):7542-3. doi: 10.1021/ja802003h.
doi: 10.1021/ja802003h pmid: 18500805 |
| 31. |
Li J, Zheng L, Cai H , et al. Facile One-Pot synthesis of Fe3O4@Au composite nanoparticles for Dual-Mode MR/CT imaging applications. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2013; 5(20):10357-66. doi: 10.1021/am4034526.
doi: 10.1021/am4034526 pmid: 24063810 |
| 32. |
Chen J, Sun Y, Chen Q , et al. Multifunctional gold nanocomposites designed for targeted CT/MR/optical trimodal imaging of human non-small cell lung cancer cells. Nanoscale 2016; 8(28):13568-73. doi: 10.1039/c6nr03143a.
doi: 10.1039/c6nr03143a pmid: 27381000 |
| 33. |
Wang G, Zhang X, Skallberg A , et al. One-step synthesis of water-dispersible ultra-small Fe3O4 nanoparticles as contrast agents for T1 and T2 magnetic resonance imaging. Nanoscale 2014; 6(5):2953-63. doi: 10.1039/c3nr05550g.
doi: 10.1039/c3nr05550g |
| 34. |
Zeng L, Ren W, Zheng J , et al. Ultrasmall water-soluble metal-iron oxide nanoparticles as T1-weighted contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging. Phys Chem Chem Phys 2012; 14(8):2631-6. doi: 10.1039/c2cp23196d.
doi: 10.1039/c2cp23196d pmid: 22273844 |
| 35. |
Yang J, Luo Y, Xu Y , et al. Conjugation of iron oxide nanoparticles with RGD-modified dendrimers for targeted tumor MR imaging. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2015; 7(9):5420-8. doi: 10.1021/am508983n.
doi: 10.1021/am508983n pmid: 25695661 |
| 36. |
Luo Y, Yang J, Yan Y , et al. RGD-functionalized ultrasmall iron oxide nanoparticles for targeted T1-weighted MR imaging of gliomas. Nanoscale 2015; 7(34):14538-46. doi: 10.1039/C5NR04003E.
doi: 10.1039/c5nr04003e pmid: 26260703 |
| 37. |
Zhang Z, Hu Y, Yang J , et al. Facile synthesis of folic acid-modified iron oxide nanoparticles for targeted MR imaging in pulmonary tumor xenografts. Mol Imaging Biol 2016; 18(4):569-78. doi: 10.1007/s11307-015-0918-5.
doi: 10.1007/s11307-015-0918-5 pmid: 26620721 |
| 38. |
Li K, Shen M, Zheng L , et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of glioma with novel APTS-coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res Lett 2014; 9(1):304-14. doi: 10.1186/1556-276X-9-304.
doi: 10.1186/1556-276X-9-304 pmid: 24994959 |
| 39. |
Jin J, Krishnamachary B, Barnett JD , et al. Human Cancer Cell Membrane-Coated Biomimetic Nanoparticles Reduce Fibroblast-Mediated Invasion and Metastasis and Induce T-Cells. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2019; 11(8):7850-61. doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b22309.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b22309 pmid: 30707559 |
| 40. | Clements TW, Sarsons C, Platnich CM , et al. Maltol-functionalized Fe3O4 nanoparticles as T2 magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents. Chemistry Select 2016; 1(8):1602-6. doi: 10.1002/slct.201600240. |
| [1] | 崔佳宁,赵亚男,王威,李涛. 急性ST段抬高型心肌梗死患者的梗死范围、心脏磁共振特征跟踪应变分析的区域心肌功能与梗死位置的关系[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2022, 37(4): 309-319. |
| [2] | 陆进,安韶光,马俊杰,杨月,张磊,俞鹏,陶恒,陈云帆,张浩轩. TOP2A基因对预测肝细胞癌预后的作用[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2022, 37(4): 331-339. |
| [3] | 阿泰菲•贝吉•霍扎尼, 阿米尔穆罕默德•梅拉吉哈, 马赫迪耶•苏莱曼尼. 嗅觉缺失的新冠肺炎患者嗅球的磁共振成像结果:系统综述[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2022, 37(1): 23-30. |
| [4] | 杨万水, 蒋涵羽, 刘超, 魏靖伟, 周宇, 宫鹏云, 宋彬, 田捷. 多组学技术及其在肝细胞癌中的临床应用:当前进展与未来机遇[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(3): 173-186. |
| [5] | 徐佳, 王萱, 金征宇, 王勤, 游燕, 王士阗, 钱天翼, 薛华丹. 探索应用延长至50分钟的钆赛酸二钠增强磁共振T1 Maps评价大鼠肝纤维化模型肝功能的价值:延长的肝胆期可能提供帮助[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(2): 110-119. |
| [6] | 陈琼,阳学风. 肝细胞癌靶向治疗研究进展[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(1): 57-65. |
| [7] | 王雪丹, 王世伟, 王波涛, 陈志晔. 磁共振场强对脑T2-FLAIR图像纹理特征影响的初步研究[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(3): 248-253. |
| [8] | 孙亮,张丽,张道强. 多图谱方法在脑MR图像分割中的应用[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(2): 110-119. |
| [9] | 王波涛, 刘明霞, 陈志晔. 磁共振T2加权成像纹理特征分析在脑胶质母细胞瘤与脑原发性中枢神经系统淋巴瘤鉴别诊断中的价值[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 10-17. |
| [10] | 徐佳, 王萱, 金征宇, 游燕, 王勤, 王士阗, 薛华丹. 钆塞酸二钠增强磁共振图像纹理分析对于评价大鼠肝纤维化的价值[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 24-32. |
| [11] | 王波涛, 樊文萍, 许欢, 李丽慧, 张晓欢, 王昆, 刘梦琦, 游俊浩, 陈志晔. 磁共振扩散加权成像纹理特征分析在乳腺良恶性肿瘤鉴别中的价值[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 33-37. |
| [12] | 李平, 朱亮, 王萱, 薛华丹, 吴晰, 金征宇. 影像学诊断1例III型胆总管囊肿[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(3): 194-203. |
| [13] | 陈志晔, 刘梦琦, 于生元, 马林. 多参数磁共振成像诊断小脑血管母细胞瘤1例报告[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(3): 188-193. |
| [14] | 陈志晔, 刘梦琦, 马林. 延髓发病型及脊髓发病型肌萎缩侧索硬化症患者皮层变薄模态:基于表面的形态学研究[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(2): 100-106. |
| [15] | 李丽慧, 黄厚斌, 陈志晔. 对比增强T2-FLAIR早期诊断复发性视神经炎一例报告[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(2): 130-134. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
|