Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2020, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (3): 248-253.doi: 10.24920/003713
磁共振场强对脑T2-FLAIR图像纹理特征影响的初步研究
- 解放军总医院海南医院放射科,海南 三亚,572013
-
收稿日期:2020-02-20出版日期:2020-09-30发布日期:2020-09-25 -
通讯作者:陈志晔 E-mail:yyqf@hotmail.com
Effect of MR Field Strength on the Texture Features of Cerebral T2-FLAIR Images: A Pilot Study
Wang Xuedan,Wang Shiwei,Wang Botao,Chen Zhiye( )
)
- Department of Radiology, Hainan Hospital of Chinese PLA General Hospital, Sanya, Hainan 572013, China
-
Received:2020-02-20Published:2020-09-30Online:2020-09-25 -
Contact:Chen Zhiye E-mail:yyqf@hotmail.com
摘要:
目的 探讨磁共振场强对脑部T2液体衰减反转恢复(T2-FLAIR)图像纹理特征的影响。
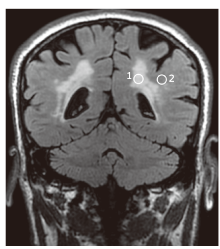
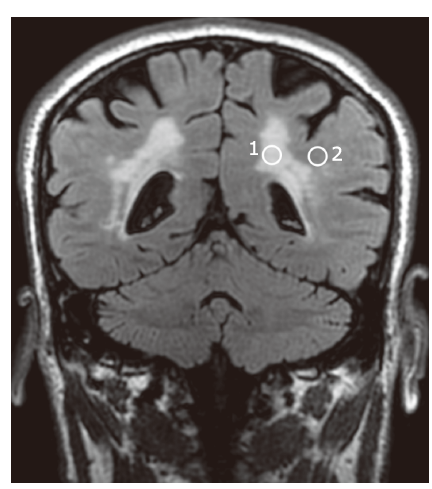
方法 我们分别采用MR-1.5T和MR-3.0T扫描对30例脑白质病变患者进行了脑部三维T2-FLAIR成像。基于ImageJ软件采用感兴趣法对白质病变区和正常白质区进行测量,并比较了MR-1.5T和MR-3.0T扫描图像所获得的纹理参数。直方图纹理特征包括平均信号强度、偏度和峰度,灰度共生矩阵纹理特征包括角二阶矩、对比度、自相关、逆差矩和熵。
结果 不论是脑白质病变区还是正常脑白质,由MR-1.5T扫描获得的平均信号强度值均显著低于MR-3.0T扫描的结果(P<0.001),而在两种场强下偏度和峰度的差异无显著性(P>0.05);此外,由MR-1.5T扫描获得的角二阶矩、自相关和逆差距均显著低于MR-3.0T扫描的结果(P<0.001),而对比度和熵均显著高于MR-3.0T扫描的结果(P<0.001)。
结论 MR场强对MR-1.5T和MR-3.0T系统所生成的脑部T2-FLAIR图像的直方图纹理无显著影响,而对灰度共生矩阵纹理特征有显著影响,此结果提示应谨慎解释不同MR场强下T2-FLAIR图像的纹理结果。
引用本文
Wang Xuedan, Wang Shiwei, Wang Botao, Chen Zhiye. Effect of MR Field Strength on the Texture Features of Cerebral T2-FLAIR Images: A Pilot Study[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(3): 248-253.
"
| Groups | Histogram | GLCM | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Meanb | Skewnessa | Kurtosisa | ASMb | Contrastb | Correlationa | IDMa | Entropya | ||
| 1.5T | 469.906 (105.600) | -0.252±0.570 | -0.358±0.790 | 0.008 (0.000) | 23.975 (26.350) | 0.009±0.005 | 0.233±0.079 | 4.956±0.320 | |
| 3.0T | 1894.024 (307.910) | -0.394±0.620 | -0.348±1.040 | 0.015 (0.010) | 8.150 (7.400) | 0.032±0.020 | 0.380±0.099 | 4.550±0.444 | |
| t/Z value | 4.762 | 1.162 | 1.059 | 4.179 | 3.898 | 6.497 | 8.385 | 4.966 | |
| P value | <0.001 | 0.245 | 0.289 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
"
| Groups | Histogram | GLCM | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Meana | Skewnessa | Kurtosisb | ASMb | Contrastb | Correlationb | IDMa | Entropya | ||
| 1.5T | 234.898±26.870 | 0.086±0.553 | -0.195 (1.330) | 0.011 (0.010) | 10.252 (9.260) | 0.023 (0.020) | 0.306±0.077 | 4.710±0.450 | |
| 3.0T | 1243.273±130.388 | -0.031±0.434 | -0.354 (0.760) | 0.025 (0.010) | 2.916 (2.530) | 0.089 (0.080) | 0.487±0.091 | 3.995±0.477 | |
| t/Z value | 45.400 | 1.089 | 1.532 | 4.683 | 4.782 | 4.710 | 10.476 | 9.754 | |
| P value | <0.001 | 0.285 | 0.125 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 1. |
Chappard D, Chennebault A, Moreau M, et al. Texture analysis of X-ray radiographs is a more reliable descriptor of bone loss than mineral content in a rat model of localized disuse induced by the Clostridium botulinum toxin. Bone 2001; 28(1):72-9. doi: 10.1016/s8756-3282(00)00438-5.
doi: 10.1016/S8756-3282(00)00438-5 |
| 2. |
Wang B, Liu M, Chen Z. Differential diagnostic value of texture feature analysis of magnetic resonance T2 weighted imaging between glioblastoma and primary central neural system lymphoma. Chin Med Sci J 2019; 34(1):10-7. doi: 10.24920/003548.
pmid: 30961775 |
| 3. |
Wang B, Fan W, Xu H, et al. Value of magnetic resonance imaging texture analysis in the differential diagnosis of benign and malignant breast tumors. Chin Med Sci J 2019; 34(1):33-7. doi: 10.24920/003516.
doi: 10.24920/003516 pmid: 30961778 |
| 4. |
Liu H, Zhou H, Zong L, et al. MRI histogram texture feature analysis of the optic nerve in the patients with optic neuritis. Chin Med Sci J 2019; 34(1):18-23. doi: 10.24920/003507.
doi: 10.24920/003507 pmid: 30961776 |
| 5. |
Wang Y, Zhang X, Wang B, et al. Value of texture analysis of intravoxel incoherent motion parameters in differential diagnosis of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor and pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Chin Med Sci J 2019; 34(1):1-9. doi: 10.24920/003531.
doi: 10.24920/003531 pmid: 30961774 |
| 6. |
Wang B, Liu G, Fan W, et al. Value of texture feature analysis in the differential diagnosis of hepatic cyst and hemangioma in magnetic resonance imaging. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao 2017; 39(2):169-76. doi: 10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.2017.02.002.
doi: 10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.2017.02.002 pmid: 28483013 |
| 7. |
Wang BT, He L, Liu G, et al. Value of magnetic resonance imaging texture feature analysis in the differential diagnosis between pancreatic serous cystadenoma and mucinous cystadenoma. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao 2018; 40(2):187-93. doi: 10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.2018.02.008.
doi: 10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.2018.02.008 pmid: 29724308 |
| 8. |
Okuda T, Korogi Y, Shigematsu Y, et al. Brain lesions: when should fluid-attenuated inversion-recovery sequences be used in MR evaluation? Radiology 1999; 212(3):793-8. doi: 10.1148/radiology.212.3.r99se07793.
pmid: 10478248 |
| 9. |
Diehl B, Najm I, Mohamed A, et al. Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery: correlations of hippocampal cell densities with signal abnormalities. Neurology 2001; 57(6):1029-32. doi: 10.1212/wnl.57.6.1029.
doi: 10.1212/wnl.57.6.1029 pmid: 11571329 |
| 10. |
Brant-Zawadzki M, Atkinson D, Detrick M, et al. Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) for assessment of cerebral infarction. Initial clinical experience in 50 patients. Stroke 1996; 27(7):1187-91. doi: 10.1161/01.str.27.7.1187.
doi: 10.1161/01.str.27.7.1187 pmid: 8685926 |
| 11. |
Bakshi R, Ariyaratana S, Benedict RH, et al. Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery magnetic resonance imaging detects cortical and juxtacortical multiple sclerosis lesions. Arch Neurol 2001; 58(5):742-8. doi: 10.1001/archneur.58.5.742.
doi: 10.1001/archneur.58.5.742 pmid: 11346369 |
| 12. |
Sikio M, Holli-Helenius KK, Harrison LC, et al. MR image texture in Parkinson’s disease: a longitudinal study. Acta Radiol 2015; 56(1):97-104. doi: 10.1177/0284185113519775.
pmid: 24413223 |
| 13. |
Sikio M, Holli KK, Harrison LC, et al. Parkinson’s disease: interhemispheric textural differences in MR images. Acad Radiol 2011; 18(10):1217-24. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2011.06.007.
pmid: 21784670 |
| 14. |
Jafari-Khouzani K, Elisevich K, Patel S, et al. FLAIR signal and texture analysis for lateralizing mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Neuroimage 2010; 49(2):1559-71. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.08.064.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.08.064 pmid: 19744564 |
| 15. |
Huppertz HJ, Wagner J, Weber B, et al. Automated quantitative FLAIR analysis in hippocampal sclerosis. Epilepsy Res 2011; 97(1-2):146-56. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2011.08.001.
doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2011.08.001 |
| 16. |
Rui W, Ren Y, Wang Y, et al. MR textural analysis on T2 FLAIR images for the prediction of true oligodendroglioma by the 2016 WHO genetic classification. J Magn Reson Imaging 2018; 48(1):74-83. doi: 10.1002/jmri.25896.
doi: 10.1002/jmri.25896 pmid: 29140606 |
| 17. |
Maubon AJ, Ferru JM, Berger V, et al. Effect of field strength on MR images: comparison of the same subject at 0.5, 1.0, and 1.5 T. Radiographics 1999; 19(4):1057-67. doi: 10.1148/radiographics.19.4.g99jl281057.
doi: 10.1148/radiographics.19.4.g99jl281057 pmid: 10464808 |
| 18. | Wenping F, Xue W, Botao W, et al. Effect of magnetic resonance field intensity on texture characteristics of T1WI structural image in brain. Chin J Med Imaging 2019; 27(4):245-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5185.2019.04.002. |
| 19. |
Fazekas F, Kleinert R, Offenbacher H, et al. Pathologic correlates of incidental MRI white matter signal hyperintensities. Neurology 1993; 43(9):1683-9. doi: 10.1212/WNL.43.9.1683
doi: 10.1212/wnl.43.9.1683 pmid: 8414012 |
| 20. |
Ding JR, Ding X, Hua B, et al. Abnormal functional connectivity density in patients with ischemic white matter lesions: an observational study. Medicine 2016; 95(36):e4625. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000004625.
doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000004625 pmid: 27603353 |
| 21. |
Ding X, Ding J, Hua B, et al. Abnormal cortical functional activity in patients with ischemic white matter lesions: a resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Neurosci Lett 2017; 644:10-7. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2017.02.015.
doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2017.02.015 pmid: 28189742 |
| 22. |
Gillies RJ, Kinahan PE, Hricak H. Radiomics: images are more than pictures, they are data. Radiology 2016; 278(2):563-77. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2015151169.
doi: 10.1148/radiol.2015151169 pmid: 26579733 |
| 23. |
Nowosielski M, Recheis W, Goebel G, et al. ADC histograms predict response to anti-angiogenic therapy in patients with recurrent high-grade glioma. Neuroradiology 2011; 53(4):291-302. doi: 10.1007/s00234-010-0808-0.
pmid: 21125399 |
| 24. |
Kamiya A, Murayama S, Kamiya H, et al. Kurtosis and skewness assessments of solid lung nodule density histograms: differentiating malignant from benign nodules on CT. Jpn J Radiol 2014; 32(1):14-21. doi: 10.1007/s11604-013-0264-y.
doi: 10.1007/s11604-013-0264-y pmid: 24248771 |
| 25. | Westfall PH. Kurtosis as peakedness, 1905-2014. R.I.P. Am Stat 2014; 68(3):191-5. doi: 10.1080/00031305.2014.917055. |
| 26. |
Ren J, Yuan Y, Wu Y, et al. Differentiation of orbital lymphoma and idiopathic orbital inflammatory pseudotumor: combined diagnostic value of conventional MRI and histogram analysis of ADC maps. BMC Med Imaging 2018; 18(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s12880-018-0246-8.
doi: 10.1186/s12880-018-0246-8 pmid: 29716527 |
| 27. |
Lai CC, Huang PH, Wang FN, et al. Histogram analysis of prostate cancer on dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging: a preliminary study emphasizing on zonal difference. PLoS One 2019; 14(2):e0212092. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0212092.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0212092 pmid: 30753222 |
| 28. |
Kim H, Park SH, Kim EK, et al. Histogram analysis of gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI for quantitative hepatic fibrosis measurement. PLoS One 2014; 9(12):e114224. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0114224.
pmid: 25460180 |
| 29. |
Chen Z, Chen X, Liu M, et al. Texture features of periaqueductal gray in the patients with medication-overuse headache. J Headache Pain 2017; 18(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s10194-017-0727-0.
pmid: 28155029 |
| [1] | 阿泰菲•贝吉•霍扎尼, 阿米尔穆罕默德•梅拉吉哈, 马赫迪耶•苏莱曼尼. 嗅觉缺失的新冠肺炎患者嗅球的磁共振成像结果:系统综述[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2022, 37(1): 23-30. |
| [2] | 杨万水, 蒋涵羽, 刘超, 魏靖伟, 周宇, 宫鹏云, 宋彬, 田捷. 多组学技术及其在肝细胞癌中的临床应用:当前进展与未来机遇[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(3): 173-186. |
| [3] | 徐佳, 王萱, 金征宇, 王勤, 游燕, 王士阗, 钱天翼, 薛华丹. 探索应用延长至50分钟的钆赛酸二钠增强磁共振T1 Maps评价大鼠肝纤维化模型肝功能的价值:延长的肝胆期可能提供帮助[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(2): 110-119. |
| [4] | 吴建强, 秦伟伟, 潘利, 王小蓉, 张彪, 单广良, 高友鹤. 中国不同地区健康人尿液蛋白质组的地域差异[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(3): 157-167. |
| [5] | 王波涛, 刘明霞, 陈志晔. 磁共振T2加权成像纹理特征分析在脑胶质母细胞瘤与脑原发性中枢神经系统淋巴瘤鉴别诊断中的价值[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 10-17. |
| [6] | 徐佳, 王萱, 金征宇, 游燕, 王勤, 王士阗, 薛华丹. 钆塞酸二钠增强磁共振图像纹理分析对于评价大鼠肝纤维化的价值[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 24-32. |
| [7] | 王波涛, 樊文萍, 许欢, 李丽慧, 张晓欢, 王昆, 刘梦琦, 游俊浩, 陈志晔. 磁共振扩散加权成像纹理特征分析在乳腺良恶性肿瘤鉴别中的价值[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 33-37. |
| [8] | 李平, 朱亮, 王萱, 薛华丹, 吴晰, 金征宇. 影像学诊断1例III型胆总管囊肿[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(3): 194-203. |
| [9] | 陈志晔, 刘梦琦, 于生元, 马林. 多参数磁共振成像诊断小脑血管母细胞瘤1例报告[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(3): 188-193. |
| [10] | 陈志晔, 刘梦琦, 马林. 延髓发病型及脊髓发病型肌萎缩侧索硬化症患者皮层变薄模态:基于表面的形态学研究[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(2): 100-106. |
| [11] | 李丽慧, 黄厚斌, 陈志晔. 对比增强T2-FLAIR早期诊断复发性视神经炎一例报告[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(2): 130-134. |
| [12] | 陈志晔,刘梦琦,马林. 延髓发病型及脊髓发病型肌萎缩侧索硬化症脑部磁共振结构特征变化[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(1): 20-28. |
| [13] | 刘梦琦, 陈志晔, 马林. 三维伪连续动脉自旋标记序列的可重复性:不同功能状态的健康成人在不同标记时间的脑容积灌注成像[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(1): 38-44. |
| [14] | 陈志晔, 刘梦琦, 马林. 基于表面的形态测量学:3T与7T高分辨磁共振结构成像受试者内比较[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2017, 32(4): 226-231. |
| [15] | 董德鑫, 纪志刚, 李汉忠, 严维刚, 张玉石. 磁珠联合基质辅助激光解吸电离飞行时间质谱技术检测肾透明细胞癌尿液差异蛋白的初步应用[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2017, 32(4): 248-252. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
|