Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2019, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (1): 24-32.doi: 10.24920/003562
钆塞酸二钠增强磁共振图像纹理分析对于评价大鼠肝纤维化的价值
徐佳1,王萱1,*( ),金征宇1,*(
),金征宇1,*( ),游燕2,王勤1,王士阗1,薛华丹1
),游燕2,王勤1,王士阗1,薛华丹1
- 1 中国医学科学院 北京协和医学院 北京协和医院 放射科 北京 100730
2 中国医学科学院 北京协和医学院 北京协和医院 病理科,北京 100730
-
收稿日期:2019-01-21修回日期:2019-03-11出版日期:2019-03-30发布日期:2019-04-08 -
通讯作者:王萱,金征宇 E-mail:dr_wangxuan@163.com;jinzy_pumch@foxmail.com
Value of Texture Analysis on Gadoxetic Acid-enhanced MR for Detecting Liver Fibrosis in a Rat Model
Xu Jia1,Wang Xuan1,*( ),Jin Zhengyu1,*(
),Jin Zhengyu1,*( ),You Yan2,Wang Qin1,Wang Shitian1,Xue Huadan1
),You Yan2,Wang Qin1,Wang Shitian1,Xue Huadan1
- 1 Department of Radiology,Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Peking Union Medical College & Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing 100730, China
2 Department of Pathology, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Peking Union Medical College & Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing 100730, China
-
Received:2019-01-21Revised:2019-03-11Published:2019-03-30Online:2019-04-08 -
Contact:Wang Xuan,Jin Zhengyu E-mail:dr_wangxuan@163.com;jinzy_pumch@foxmail.com
摘要:
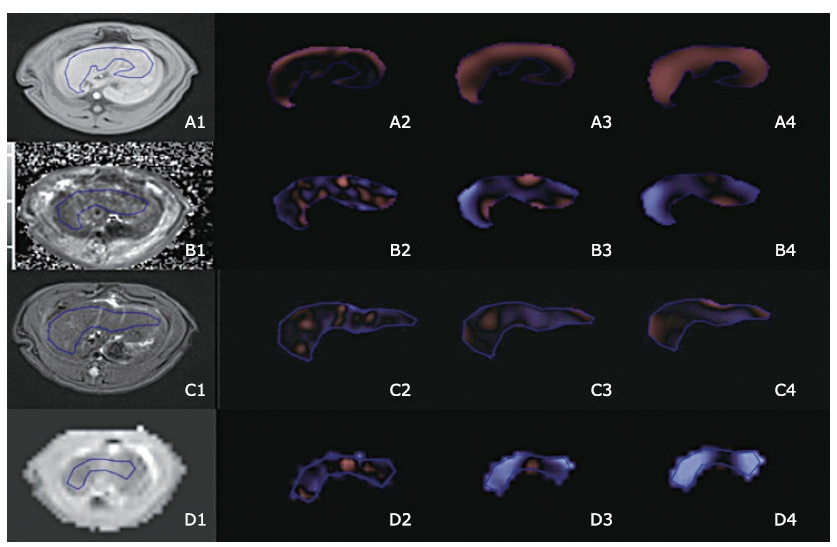
目的 对钆塞酸二钠增强磁共振T1 mapping成像以及T1加权成像(T1W)、T2加权成像(T2W)、表观扩散系数(ADC)图像进行纹理分析,探讨其在大鼠模型中定量评价肝纤维化的价值。
方法 采用四氯化碳腹腔注射法构建大鼠肝纤维化模型,打药时长4~12周(n=30),在对照组中(n=10)注射等量生理盐水。磁共振扫描序列包括T2W,弥散加权成像,注射对比剂前后的T1W和T1 mapping系列图像。利用METAVIR分级将肝纤维化分为正常(F0),轻度肝纤维化(F1~2)和重度肝纤维化(F3~4)。纹理特征参数包括平均灰度强度,标准差,熵,正象素均值、偏斜和峰度。采用非参数Mann-Whitney U检验比较各个序列的上述各项纹理参数在F0与F ≥ 1间、以及F0~2与F3~4间的差异。利用受试者工作特征曲线(ROC)分析纹理参数在区分正常肝组织和肝纤维化、F0~2和F3~4的诊断准确性,并获得ROC曲线下面积(AUC)以评价纹理参数的诊断价值。
结果 20只大鼠完成磁共振T1 mapping扫描,其病理结果为正常(F0,n=6),轻度肝纤维化(F1~2,n=5) 和重度肝纤维化(F3~4,n=9)。在打药前T1 mapping图像中,在各个空间尺度因子(spatial scaling factor,SSF)下,F≥1组的熵值均显著大于F0组(P= 0.015,0.015,0.015,0.013,0.015,0.018,分别对应于SSF = 0,2,3,4,5,6);在SSF 4,5,6下,F≥1组的平均灰度强度显著高于F0组(P= 0.004,0.006,0.013)。在区分正常和肝纤维化组时,打药前T1 mapping图像的熵和平均灰度强度在大多数SSF下,展现出中等诊断价值。
结论 部分钆塞酸二钠增强磁共振图像的纹理参数,特别是打药前T1 mapping图像的熵,对于肝纤维化的诊断具有一定价值。
引用本文
Xu Jia, Wang Xuan, Jin Zhengyu, You Yan, Wang Qin, Wang Shitian, Xue Huadan. Value of Texture Analysis on Gadoxetic Acid-enhanced MR for Detecting Liver Fibrosis in a Rat Model[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 24-32.
"
| Comparison | Sequence | Texture parameter | SSF | Uvalue | Pvalue |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F0 vs. F1-4 | Pre-contrast T1 mapping | Mean | 4 | 114.0 | 0.004 |
| 5 | 113.0 | 0.006 | |||
| 6 | 109.0 | 0.013 | |||
| Entropy | 0 | 108.0 | 0.015 | ||
| 2 | 107.5 | 0.015 | |||
| 3 | 108.0 | 0.015 | |||
| 4 | 114.0 | 0.013 | |||
| 5 | 113.0 | 0.015 | |||
| 6 | 109.0 | 0.018 | |||
| Post-contrast T1 mapping (20 min) | Mean | 6 | 21.0 | 0.039 | |
| Post-contrast T1 mapping (60 min) | Kurtosis | 6 | 76.5 | 0.025 | |
| F0-2 vs. F3-4 | Pre-contrast T1 mapping | Skewness | 4 | 103.0 | 0.036 |
"
| Comparison | Sequence | Texture parameter | SSF | U value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F0 vs. F1-4 | Pre-contrast T1W | Mean | 2 | 39.0 | 0.045 |
| 3 | 35.0 | 0.025 | |||
| 4 | 37.0 | 0.034 | |||
| MPP | 3 | 34.0 | 0.021 | ||
| 4 | 33.0 | 0.018 | |||
| Post-contrast T1W (20 min) | SD | 0 | 98.0 | 0.013 | |
| Entropy | 0 | 94.5 | 0.023 | ||
| Kurtosis | 2 | 98.5 | 0.011 | ||
| Post-contrast T1W (60 min) | SD | 0 | 40.0 | 0.018 | |
| Entropy | 0 | 39.5 | 0.028 | ||
| MPP | 3 | 6.0 | 0.040 | ||
| 4 | 6.0 | 0.040 | |||
| Skewness | 3 | 41.0 | 0.010 | ||
| 4 | 40.0 | 0.018 | |||
| F0-2 vs. F3-4 | Pre-contrast T1W | Skewness | 0 | 122.0 | 0.041 |
| Post-contrast T1W (20 min) | SD | 0 | 112.0 | 0.004 | |
| Entropy | 0 | 101.5 | 0.027 | ||
| Kurtosis | 2 | 103.0 | 0.023 | ||
| Post-contrast T1W (60 min) | SD | 0 | 52.0 | 0.004 | |
| Entropy | 0 | 51.5 | 0.004 |
"
| Sequence | Comparison | Texture parameter | SSF | AUC | 95%CI | Pvalue | Threshold | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-contrast T1 mapping | F0 vs. F1-4 | Mean | 4 | 0.857 | 0.711, 1.000 | 0.006 | >-391.855 | 0.684 | 1.000 |
| 5 | 0.850 | 0.701, 0.999 | 0.007 | >-608.24 | 0.789 | 1.000 | |||
| 6 | 0.820 | 0.635, 1.000 | 0.014 | >-745.89 | 0.789 | 0.857 | |||
| Entropy | 0 | 0.812 | 0.638, 0.986 | 0.016 | >5.305 | 0.632 | 1.000 | ||
| 2 | 0.808 | 0.631, 0.985 | 0.018 | >5.655 | 0.632 | 0.857 | |||
| 3 | 0.812 | 0.636, 0.988 | 0.016 | >5.210 | 0.632 | 0.857 | |||
| 4 | 0.816 | 0.641, 0.991 | 0.015 | >5.185 | 0.632 | 0.857 | |||
| 5 | 0.812 | 0.637, 0.987 | 0.016 | >5.225 | 0.632 | 0.857 | |||
| 6 | 0.805 | 0.629, 0.980 | 0.019 | >5.170 | 0.632 | 0.857 | |||
| F0-2 vs.F3-4 | Skewness | 4 | 0.747 | 0.554, 0.939 | 0.037 | >-0.265 | 0.900 | 0.625 | |
| Post-contrast T1 mapping (60 min) | F0 vs. F1-4 | Kurtosis | 6 | 0.797 | 0.592, 1.000 | 0.028 | >-0.390 | 0.833 | 0.750 |
"
| Sequence | Comparison | Texture parameter | SSF | AUC | 95%CI | Pvalue | Threshold | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-contrast T1W | F0 vs. F1-4 | Mean | 2 | 0.745 | 0.556, 0.934 | 0.043 | <131.57 | 0.765 | 0.556 |
| 3 | 0.771 | 0.586, 0.856 | 0.025 | <186.005 | 0.706 | 0.778 | |||
| 4 | 0.758 | 0.561, 0.955 | 0.033 | <255 | 0.647 | 0.556 | |||
| MPP | 3 | 0.778 | 0.592, 0.964 | 0.022 | <227.22 | 0.706 | 0.778 | ||
| 4 | 0.784 | 0.600, 0.969 | 0.019 | <320.61 | 0.765 | 0.667 | |||
| Post-contrast T1W (20 min) | F0 vs. F1-4 | SD | 0 | 0.817 | 0.642, 0.991 | 0.014 | >53.785 | 0.667 | 1.000 |
| Entropy | 0 | 0.788 | 0.599, 0.976 | 0.026 | >5.04 | 0.667 | 0.825 | ||
| Kurtosis | 2 | 0.821 | 0.644, 0.998 | 0.013 | >0.700 | 0.600 | 0.875 | ||
| F0-2 vs. F3-4 | SD | 0 | 0.848 | 0.689, 1.000 | 0.005 | >53.785 | 0.727 | 0.833 | |
| Entropy | 0 | 0.769 | 0,572, 0.966 | 0.029 | >5.04 | 0.727 | 0.750 | ||
| Kurtosis | 2 | 0.780 | 0.582, 0.979 | 0.023 | >0.155 | 0.818 | 0.593 | ||
| Post-contrast TIW (60 min) | F0 vs. F1-4 | SD | 0 | 0.909 | 0.739, 1.000 | 0.019 | >36.375 | 0.909 | 1.000 |
| Entropy | 0 | 0.898 | 0.735, 1.000 | 0.022 | >4.920 | 0.727 | 1.000 | ||
| MPP | 3 | 0.864 | 0.670, 1.000 | 0.037 | <303.140 | 0.909 | 0.750 | ||
| 4 | 0.864 | 0.671, 1.000 | 0.037 | <351.545 | 0.818 | 1.000 | |||
| Skewness | 3 | 0.932 | 0.794, 1.000 | 0.013 | >-0.115 | 0.909 | 1.000 | ||
| 4 | 0.909 | 0.754, 1.000 | 0.019 | >-0.160 | 0.818 | 1.000 | |||
| F0-2 vs. F3-4 | SD | 0 | 0.929 | 0.782, 1.000 | 0.005 | >37.345 | 1.000 | 0.857 | |
| Entropy | 0 | 0.920 | 0.781, 1.000 | 0.007 | >4.920 | 0.875 | 0.857 | ||
| 3 | 0.804 | 0.569, 1.000 | 0.049 | >6.050 | 0.750 | 0.857 | |||
| 4 | 0.804 | 0.573, 1.000 | 0.049 | >6.095 | 0.625 | 0.857 |
| 1. |
Afdhal NH, Nunes D . Evaluation of liver fibrosis: a concise review. Am J Gastroenterol 2004; 99(6):1160-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2004.30110.x.
doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2004.30110.x pmid: 15180741 |
| 2. |
Nguyen D, Talwalkar JA . Noninvasive assessment of liver fibrosis. Hepatology 2011; 53(6):2107-10. doi: 10.1002/hep.24401.
doi: 10.1002/hep.24013 pmid: 21254180 |
| 3. |
Lubner MG, Smith AD, Sandrasegaran K , et al. CT texture analysis: definitions, applications, biologic correlates, and challenges. RadioGraphics 2017; 37(5):1483-503. doi: 10.1148/rg.2017170056.
doi: 10.1148/rg.2017170056 pmid: 28898189 |
| 4. |
Fujimoto K, Tonan T, Azuma S , et al. Evaluation of the mean and entropy of apparent diffusion coefficient values in chronic hepatitis C: correlation with pathologic fibrosis stage and inflammatory activity grade. Radiology 2011; 258(3):739-48. doi: 10.1148/radiol.10100853.
doi: 10.1148/radiol.10100853 pmid: 21248235 |
| 5. |
Barry B, Buch K, Soto JA , et al. Quantifying liver fibrosis through the application of texture analysis to diffusion weighted imaging. Magn Reson Imaging 2014; 32(1):84-90. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2013.04.006.
doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2013.04.006 pmid: 24239337 |
| 6. |
Bahl G, Cruite I, Wolfson T , et al. Noninvasive classification of hepatic fibrosis based on texture parameters from double contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance images. J Magn Reson Imaging 2012; 36(5):1154-61. doi: 10.1002/jmri.23759.
doi: 10.1002/jmri.23759 pmid: 22851409 |
| 7. |
Jirák D, Dezortová M, Taimr P , et al. Texture analysis of human liver. J Magn Reson Imaging 2002; 15(1):68-74.
doi: 10.1002/jmri.10042 pmid: 11793459 |
| 8. |
Katsube T, Okada M, Kumano S , et al. Estimation of liver function using T1 mapping on Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Invest Radiol 2011; 46(4):277-83. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0b013e318200f67d.
doi: 10.1097/RLI.0b013e3182804f84 pmid: 21343827 |
| 9. |
Zhou ZP, Long LL, Huang LJ , et al. Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI T1 mapping for assessment of liver function in rabbit fibrosis model: comparison of hepatobiliary phase images obtained at 10 and 20 min. Radiol Med 2017; 122(4):239-47. doi: 10.1007/s11547-016-0719-1.
doi: 10.1007/s11547-016-0719-1 |
| 10. |
Zhou ZP, Long LL, Qiu WJ , et al. Comparison of 10- and 20-min hepatobiliary phase images on Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI T1 mapping for liver function assessment in clinic. Abdom Radiol (NY) 2017; 42(9):2272-8. doi: 10.1007/s00261-017-1143-2.
doi: 10.1007/s00261-017-1143-2 pmid: 28396918 |
| 11. |
Ding Y, Rao SX, Zhu T , et al. Liver fibrosis staging using T1 mapping on gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI compared with DW imaging. Clin Radiol 2015; 70(10):1096-103. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2015.04.014.
doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2015.04.014 pmid: 26164421 |
| 12. |
Pan S, Wang XQ, Guo QY . Quantitative assessment of hepatic fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B and C: T1 mapping on Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced liver magnetic resonance imaging. WJG 2018; 24(18):2024-35. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i18.2024.
doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i18.2024 pmid: 29760545 |
| 13. |
Intraobserver and interobserver variations in liver biopsy interpretation in patients with chronic hepatitis C. The French METAVIR Cooperative Study Group. Hepatology 1994; 20(1 Pt 1):15-20.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1527-3350 |
| 14. |
Ganeshan B, Miles KA . Quantifying tumour heterogeneity with CT. Cancer Imaging 2013; 13(1):140-9. doi: 10.1102/1470-7330.2013.0015.
doi: 10.1102/1470-7330.2013.0015 pmid: 23545171 |
| 15. |
Lubner MG, Malecki K, Kloke J , et al. Texture analysis of the liver at MDCT for assessing hepatic fibrosis. Abdom Radiol (NY) 2017; 42(8):2069-78. doi: 10.1007/s00261-017-1096-5.
doi: 10.1007/s00261-017-1096-5 pmid: 28314916 |
| 16. |
Raman SP, Schroeder JL, Huang P , et al. Preliminary data using computed tomography texture analysis for the classification of hypervascular liver lesions: generation of a predictive model on the basis of quantitative spatial frequency measurements—a work in progress. J Comput Assist Tomogr 2015; 39(3):383-95. doi: 10.1097/RCT.0000000000000217.
doi: 10.1097/RCT.0000000000000217 pmid: 25700222 |
| 17. |
Cannella R, Rangaswamy B, Minervini MI , et al. Value of texture analysis on gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI for differentiating hepatocellular adenoma from focal nodular hyperplasia. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2019; 212(3):538-46. doi: 10.2214/AJR.18.20182.
doi: 10.2214/AJR.18.20182 |
| 18. |
Mulé S, Thiefin G, Costentin C , et al. Advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: pretreatment contrast-enhanced CT texture parameters as predictive biomarkers of survival in patients treated with sorafenib. Radiology 2018; 288(2):445-55. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2018171320.
doi: 10.1148/radiol.2018171320 |
| 19. |
Chen S, Zhu Y, Liu Z , et al. Texture analysis of baseline multiphasic hepatic computed tomography images for the prognosis of single hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy: a retrospective pilot study. Eur J Radiol 2017; 90:198-204. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2017.02.035.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2017.02.035 pmid: 28583634 |
| 20. |
Canellas R, Mehrkhani F, Patino M , et al. Characterization of portal vein thrombosis (neoplastic versus bland) on CT images using software-based texture analysis and thrombus density (Hounsfield Units). AJR Am J Roentgenol 2016; 207(5):W81-7. doi: 10.2214/AJR.15.15928.
doi: 10.2214/AJR.15.15928 pmid: 27490095 |
| 21. |
Sadot E, Simpson AL, Do RKG , et al. Cholangiocarcinoma: correlation between molecular profiling and imaging phenotypes. PLoS One 2015; 10(7):e0132953. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132953.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132953 pmid: 26207380 |
| 22. |
Daginawala N, Li B, Buch K , et al. Using texture analyses of contrast enhanced CT to assess hepatic fibrosis. Eur J Radiol 2016; 85(3):511-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2015.12.009.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2015.12.009 pmid: 26860661 |
| 23. |
Romero-Gómez M, Gómez-González E, Madrazo A , et al. Optical analysis of computed tomography images of the liver predicts fibrosis stage and distribution in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2008; 47(3):810-6. doi: 10.1002/hep.22112.
doi: 10.1002/hep.22112 pmid: 18098299 |
| 24. |
Zhang X, Gao X, Liu BJ , et al. Effective staging of fibrosis by the selected texture features of liver: which one is better, CT or MR imaging? Comput Med Imaging Graph 2015; 46 Pt 2: 227-36. doi: 10.1016/j.compmedimag.2015.09.003.
doi: 10.1016/j.compmedimag.2015.09.003 pmid: 26455963 |
| 25. | Jirák D, Dezortová M, Taimr P , et al. Texture analysis of human liver. J Magn Reson Imaging 2002; 15(1):68-74. |
| 26. |
Lubner MG, Stabo N, Lubner SJ , et al. CT textural analysis of hepatic metastatic colorectal cancer: pre-treatment tumor heterogeneity correlates with pathology and clinical outcomes. Abdom Imaging 2015; 40(7):2331-7. doi: 10.1007/s00261-015-0438-4.
doi: 10.1007/s00261-015-0438-4 pmid: 25968046 |
| 27. |
Ng F, Kozarski R, Ganeshan B , et al. Assessment of tumor heterogeneity by CT texture analysis: can the largest cross-sectional area be used as an alternative to whole tumor analysis? Eur J Radiol 2013; 82(2):342-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2012.10.023.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2012.10.023 pmid: 23194641 |
| 28. |
Yoon JH, Lee JM, Paek M , et al. Quantitative assessment of hepatic function: modified look-locker inversion recovery (MOLLI) sequence for T1 mapping on Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced liver MR imaging. Eur Radiol 2016; 26(6):1775-82. doi: 10.1007/s00330-015-3994-7.
doi: 10.1007/s00330-015-3994-7 pmid: 26373756 |
| 29. |
Yoon JH, Lee JM, Kang H-J , et al. Quantitative assessment of liver function by using gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI: hepatocyte uptake ratio. Radiology 2019; 290(1):125-33. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2018180753.
doi: 10.1148/radiol.2018180753 |
| [1] | 阿泰菲•贝吉•霍扎尼, 阿米尔穆罕默德•梅拉吉哈, 马赫迪耶•苏莱曼尼. 嗅觉缺失的新冠肺炎患者嗅球的磁共振成像结果:系统综述[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2022, 37(1): 23-30. |
| [2] | 徐佳, 王萱, 金征宇, 王勤, 游燕, 王士阗, 钱天翼, 薛华丹. 探索应用延长至50分钟的钆赛酸二钠增强磁共振T1 Maps评价大鼠肝纤维化模型肝功能的价值:延长的肝胆期可能提供帮助[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(2): 110-119. |
| [3] | 曹剑, 王国蓉, 王志伟, 金征宇. CT纹理分析:结直肠癌KRAS基因突变状态评估的潜在生物标志物[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(4): 306-314. |
| [4] | 王雪丹, 王世伟, 王波涛, 陈志晔. 磁共振场强对脑T2-FLAIR图像纹理特征影响的初步研究[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(3): 248-253. |
| [5] | 王英伟, 张兴华, 王波涛, 王叶, 刘梦琦, 王海屹, 叶慧义. 体素内不相干运动成像参数的纹理分析在胰腺神经内分泌肿瘤和胰腺癌鉴别诊断中的价值[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 1-9. |
| [6] | 王波涛, 刘明霞, 陈志晔. 磁共振T2加权成像纹理特征分析在脑胶质母细胞瘤与脑原发性中枢神经系统淋巴瘤鉴别诊断中的价值[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 10-17. |
| [7] | 刘洪娟, 周欢粉, 宗林雄, 刘梦琦, 魏世辉, 陈志晔. 视神经炎患者视神经磁共振成像直方图分析[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 18-23. |
| [8] | 王波涛, 樊文萍, 许欢, 李丽慧, 张晓欢, 王昆, 刘梦琦, 游俊浩, 陈志晔. 磁共振扩散加权成像纹理特征分析在乳腺良恶性肿瘤鉴别中的价值[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 33-37. |
| [9] | 王国蓉, 王志伟, 金征宇. 纹理分析在结直肠癌新辅助放化疗疗效预测及预后分析中的应用及研究进展[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 45-50. |
| [10] | 李平, 朱亮, 王萱, 薛华丹, 吴晰, 金征宇. 影像学诊断1例III型胆总管囊肿[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(3): 194-203. |
| [11] | 陈志晔, 刘梦琦, 于生元, 马林. 多参数磁共振成像诊断小脑血管母细胞瘤1例报告[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(3): 188-193. |
| [12] | 陈志晔, 刘梦琦, 马林. 延髓发病型及脊髓发病型肌萎缩侧索硬化症患者皮层变薄模态:基于表面的形态学研究[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(2): 100-106. |
| [13] | 李丽慧, 黄厚斌, 陈志晔. 对比增强T2-FLAIR早期诊断复发性视神经炎一例报告[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(2): 130-134. |
| [14] | 陈志晔,刘梦琦,马林. 延髓发病型及脊髓发病型肌萎缩侧索硬化症脑部磁共振结构特征变化[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(1): 20-28. |
| [15] | 刘梦琦, 陈志晔, 马林. 三维伪连续动脉自旋标记序列的可重复性:不同功能状态的健康成人在不同标记时间的脑容积灌注成像[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(1): 38-44. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
|