Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2020, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (2): 135-141.doi: 10.24920/003618
• Original Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
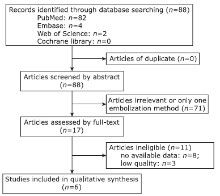
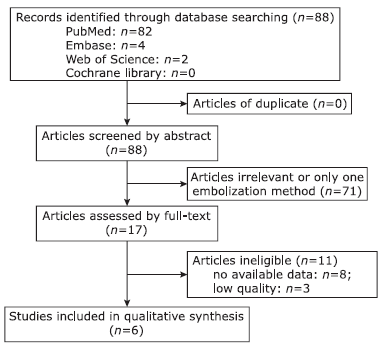
Transarterial Embolization versus Translumber Embolization for Type Ⅱ Endoleak after Endovascular Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair: A Meta-Analysis
Zhang Xu, Ji Lei, Chen Mengyin, Wang Wei, Zheng Yuehong( )
)
- Department of Vascular Surgery, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Science & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100730, China
-
Received:2019-04-02Accepted:2019-10-07Published:2020-06-30Online:2019-06-12 -
Contact:Zheng Yuehong E-mail:yuehongzheng@yahoo.com
Cite this article
Zhang Xu,Ji Lei,Chen Mengyin,Wang Wei,Zheng Yuehong. Transarterial Embolization versus Translumber Embolization for Type Ⅱ Endoleak after Endovascular Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair: A Meta-Analysis[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(2): 135-141.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Table 1
The basic information of the included studies on TA embolization and TL embolization for type Ⅱ endoleak"
| Studies | Country | Research type | Criteria for intervention | No. of patients | No. of endoleaks | TA | TL | Materials | Follow-up | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Technical success | Clinical success | Technical success | Clinical success | |||||||||
| Marcelin et al., 2017 [ | France | Retrospective study | Persistent after 6 months and increasing sac size > 5 mm | 28 | 29 | 16/22 (72.7%) | NS | 1/7 (14.3%) | NS | onyx | 20 ± 12 months (range 6 - 49 months) | |
| Haq et al., 2017 [ | UK | Retrospective study | Increasing sac size > 5 mm | 28 | 28 | 7/17 (41.2%) | 2/17 (11.8%) | 3/11 (27.3%) | 3/11 (27.3%) | coils or embolizing agent | 3.11 years (median) | |
| Massis et al., 2012 [ | USA | Retrospective study | Increase of sac size > 5 mm within 6 month, or sac > 6 cm or change in sac morphology, or change in position or orientation of stent graft in sac | 95 | 101 | 58/65 (89.2%) | 21/29 (72.4%) | 36/36 (100%) | 18/24 (75%) | onyx | 15 weeks | |
| Nevala et al., 2010 [ | Finland | Retrospective study | Increasing sac size or persistent after 3 months | 14 | 14 | 4/10 (40%) | 2/9 (22.2%) | 3/3 (100%) | 3/3 (100%) | coils, thrombin, gelatin, onyx, glue | NS | |
| Stavropoulos et al., 2009 [ | USA | Retrospective study | Persistent > 1 month and aneurysm expansion | 84 | 85 | 22/23 (95.7%) | 18/23 (78.3%) | 62/62 (100%) | 45/62 (72.6%) | coils, n-butyl cyanoacrylate | 18.7 months (range 1-84 months) | |
| Baum et al., 2002 [ | USA | Retrospective study | Persistent >1 month | 19 | 33 | 17/20 (85%) | 4/20 (20%) | 13/13 (100%) | 12/13 (92.3%) | coils, thrombin | 13.1/8.4 months | |
Table 2
Quality assessment results of included studies employing the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale"
| Studies | Adequate case definition | Represen- tativeness | Selection of controls | Definition of controls | Compara- bility | Ascertainment of exposure | Same method of ascertainment | Non-Response rate | Total score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marcelin et al., 2017[ | ★ | ★ | n/a | ★ | n/a | ★ | ★ | n/a | 5 |
| Haq et al., 2017[ | ★ | ★ | n/a | ★ | ★ | ★ | ★ | n/a | 6 |
| Massis et al., 2012[ | ★ | ★ | n/a | ★ | n/a | ★ | ★ | n/a | 5 |
| Nevala et al., 2010[ | ★ | ★ | n/a | ★ | n/a | ★ | ★ | n/a | 5 |
| Stavropoulos et al., 2009[ | ★ | ★ | n/a | ★ | ★ | ★ | ★ | n/a | 6 |
| Baum et al., 2002[ | ★ | ★ | n/a | ★ | ★ | ★ | ★ | n/a | 6 |
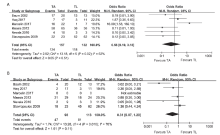
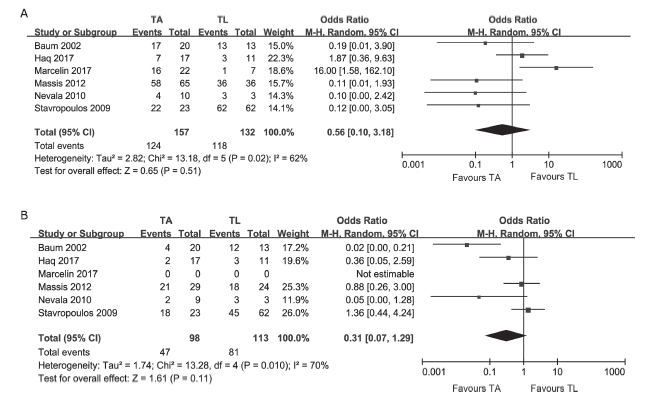
Figure 2.
Forest plot showing the pooled odds ratios of the studies comparing technical success and clinical success between two interventions of TA and TL in treatment of type Ⅱ endoleak. A. Comparison of the technical success rates; B. comparison of the clinical success rates. TA, transarterial (embolization); TL, translumber (embolization)."
| 1. |
LeFevre ML, Siu AL, Peters JJ , et al. Screening for abdominal aortic aneurysm: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med 2014; 161(4):281-90. doi: 10.7326/m14-1204.
doi: 10.7326/M14-1204 |
| 2. |
Patel R, Sweeting MJ, Powell JT , et al. Endovascular versus open repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm in 15-years’ follow-up of the UK endovascular aneurysm repair trial 1 (EVAR trial 1): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2016; 388(10058):2366-74. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(16)31135-7.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31135-7 pmid: 27743617 |
| 3. |
Schermerhorn ML, Buck DB, O’Malley AJ, et al. Long-term outcomes of abdominal aortic aneurysm in the medicare population. New Eng J Med 2015; 373(4):328-38. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1405778.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1405778 pmid: 26200979 |
| 4. |
Hobo R, Buth J; EUROSTAR collaborators . Secondary interventions following endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair using current endografts. A EUROSTAR report. J Vasc Surg 2006; 43(5):896-902. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2006.01.010.
doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2006.01.010 pmid: 16678679 |
| 5. |
Zandvoort HJ, Gon?alves FB, Verhagen HJ , et al. Results of endovascular repair of infrarenal aortic aneurysms using the Endurant stent graft. J Vasc Surg 2014; 59(5):1195-202. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2013.12.031.
doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2013.12.031 |
| 6. |
Kray J, Kirk S, Franko J , et al. Role of type II endoleak in sac regression after endovascular repair of infrarenal abdominal aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Surg 2015; 61(4):869-74. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2014.11.003.
doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2014.11.003 pmid: 25601501 |
| 7. |
Zhou W, Blay E Jr, Varu V , et al. Outcome and clinical significance of delayed endoleaks after endovascular aneurysm repair. J Vasc Surg 2014; 59(4):915-20. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2013.10.093.
doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2013.10.093 |
| 8. |
Chaikof EL, Brewster DC, Dalman RL , et al. The Society for Vascular Surgery practice guidelines on the care of patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Surg 2018; 67(1):2-77. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2017.10.044.
doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2017.10.044 pmid: 29268916 |
| 9. |
Jones JE, Atkins MD, Brewster DC ,et al. Persistent type 2 endoleak after endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm is associated with adverse late outcomes. J Vasc Surg 2007; 46(1):1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2007.02.073.
doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2007.02.073 |
| 10. |
Sidloff DA, Stather PW, Choke E, et al. Type Ⅱ endoleak after endovascular aneurysm repair. Br J Surg 2013; 100(10):1262-70. doi: 10.1002/bjs.9181.
doi: 10.1002/bjs.9181 pmid: 23939840 |
| 11. |
Ultee KHJ, Büttner S, Huurman R , et al. Editor’s Choice: Systematic review and meta-analysis of the outcome of treatment for type Ⅱ endoleak following endovascular aneurysm repair. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 2018; 56(6):794-807. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2018.06.009.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2018.06.009 pmid: 30104089 |
| 12. |
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J , et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: explanation and elaboration. BMJ 2009; 339:b2700. doi: 10.1136/bmj.b2700.
doi: 10.1136/bmj.b2700 pmid: 19622552 |
| 13. |
Parodi JC, Palmaz JC, Barone HD . Transfemoral intraluminal graft implantation for abdominal aortic aneurysms. Ann Vasc Surg 1991; 5(6):491-9. doi: 10.1007/bf02015271.
doi: 10.1007/BF02015271 pmid: 1837729 |
| 14. |
Zaiem F, Almasri J, Tello M , et al. A systematic review of surveillance after endovascular aortic repair. J Vasc Surg 2018; 67(1):320-31. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2017.04.058.
doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2017.04.058 pmid: 28662928 |
| 15. |
Gelfand DV, White GH, Wilson SE . Clinical significance of type Ⅱ endoleak after endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm. Ann Vasc Surg 2006; 20(1):69-74. doi: 10.1007/s10016-005-9382-z.
doi: 10.1007/s10016-005-9382-z |
| 16. | Choke E, Thompson M . Endoleak after endovascular aneurysm repair: current concepts. J Cardiovasc Surg 2004; 45(4):349-66. |
| 17. |
Manunga JM, Cragg A, Garberich R , et al. Preoperative inferior mesenteric artery embolization: A valid method to reduce the rate of type Ⅱ endoleak after EVAR? Ann Vasc Surg 2017; 39:40-7. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2016.05.106.
doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2016.05.106 pmid: 27531083 |
| 18. |
Walker J, Tucker LY, Goodney P , et al. Type II endoleak with or without intervention after endovascular aortic aneurysm repair does not change aneurysm-related outcomes despite sac growth. J Vasc Surg 2015; 62(3):551-61. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2015.04.389.
doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2015.04.389 pmid: 26059094 |
| 19. |
van Marrewijk CJ, Fransen G, Laheij RJ , et al. Is a type Ⅱ endoleak after EVAR a harbinger of risk? Causes and outcome of open conversion and aneurysm rupture during follow-up. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 2004; 27(2):128-37. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2003.10.016.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2003.10.016 pmid: 14718893 |
| 20. |
van der Laan MJ, Bartels LW, Viergever MA , et al. Computed tomography versus magnetic resonance imaging of endoleaks after EVAR. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 2006; 32(4):361-65. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2006.02.011.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2006.02.011 pmid: 16630731 |
| 21. |
Habets J, Zandvoort HJ, Reitsma JB , et al. Magnetic resonance imaging is more sensitive than computed tomography angiography for the detection of endoleaks after endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair: a systematic review. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 2013; 45(4):340-50. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2012.12.014.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2012.12.014 pmid: 23403221 |
| 22. |
Aziz A, Menias CO, Sanchez LA , et al. Outcomes of percutaneous endovascular intervention for type II endoleak with aneurysm expansion. J Vasc Surg 2012; 55(5):1263-67. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2011.10.131.
doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2011.10.131 |
| 23. |
Patatas K, Ling L, Dunning J , et al. Static sac size with a type Ⅱ endoleak post-endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair: surveillance or embolization? Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 2012; 15(3):462-6. doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivs201.
doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivs201 pmid: 22617500 |
| 24. |
Moll FL, Powell JT, Fraedrich G , et al. Management of abdominal aortic aneurysms clinical practice guidelines of the European society for vascular surgery. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 2011; 41(S1):S1-58. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2010.09.011.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2010.09.011 |
| 25. |
Karthikesalingam A, Thrumurthy SG, Jackson D , et al. Current evidence is insufficient to define an optimal threshold for intervention in isolated type Ⅱ endoleak after endovascular aneurysm repair. J Endovasc Ther 2012; 19(2):200-8. doi: 10.1583/11-3762R.1.
doi: 10.1583/11-3762R.1 pmid: 22545885 |
| 26. |
Arko FR, Filis KA, Siedel SA , et al. Intrasac flow velocities predict sealing of type Ⅱ endoleaks after endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. J Vasc Surg 2003; 37(1):8-15. doi: 10.1067/mva.2003.55.
doi: 10.1067/mva.2003.55 pmid: 12514572 |
| 27. |
Rial R, Serrano Fj Fj, Vega M , et al. Treatment of type II endoleaks after endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysms: translumbar puncture and injection of thrombin into the aneurysm sac. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 2004; 27(3):333-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2003.11.005.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2003.11.005 pmid: 14760606 |
| 28. |
Steinmetz E, Rubin BG, Sanchez LA , et al. Type Ⅱ endoleak after endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair: a conservative approach with selective intervention is safe and cost-effective. J Vasc Surg 2004; 39(2):306-13. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2003.10.026.
doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2003.10.026 pmid: 14743129 |
| 29. |
Stavropoulos SW, Park J, Fairman R , et al. Type 2 endoleak embolization comparison: translumbar embolization versus modified transarterial embolization. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2009; 20(10):1299-302. doi: 10.1016/j.jvir.2009.07.003.
doi: 10.1016/j.jvir.2009.07.003 |
| 30. |
Marcelin C, Le Bras Y, Petitpierre F , et al. Safety and efficacy of embolization using Onyx((R)) of persistent type II endoleaks after abdominal endovascular aneurysm repair. Diagn Interv Imaging 2017; 98(6):491-97. doi: 10.1016/j.diii.2017.01.003.
doi: 10.1016/j.diii.2017.01.003 pmid: 28196614 |
| 31. |
Haq IU, Kelay A, Davis M , et al. Ten-year single-centre experience with type Ⅱ endoleaks: Intervention versus observation. Vasc Med 2017; 22(4):316-23. doi: 10.1177/1358863x17704315.
doi: 10.1177/1358863X17704315 pmid: 28436300 |
| 32. |
Massis K, Carson WG 3rd, Rozas A, et al. Treatment of type Ⅱ endoleaks with ethylene-vinyl-alcohol copolymer (Onyx). Vasc Endovascular Surg 2012; 46(3):251-57. doi: 10.1177/1538574412442401.
doi: 10.1177/1538574412442401 pmid: 22492111 |
| 33. |
Nevala T, Biancari F, Manninen H , et al. Type II endoleak after endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm: effectiveness of embolization. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 2010; 33(4):278-84. doi: 10.1007/s00270-009-9685-5.
doi: 10.1007/s00270-009-9685-5 |
| 34. |
Baum RA, Carpenter JP, Golden MA , et al. Treatment of type 2 endoleaks after endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysms: comparison of transarterial and translumbar techniques. J Vasc Surg 2002; 35(1):23-29. doi: 10.1067/mva.2002.121068.
doi: 10.1067/mva.2002.121068 pmid: 11802129 |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|