Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2017, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (2): 75-82.doi: 10.24920/J1001-9294.2017.010
• Original Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Abnormal Alterations of Cortical Thickness in 16 Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Pilot MRI Study△
Chen Zhiye1, 2, Zang Xiujuan3, Liu Mengqi1, 2, Liu Mengyu1, Li Jinfeng1, Gu Zhaoyan4, Ma Lin1, *( )
)
- 1Department of Radiology, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100853, China
2Department of Radiology, Hainan Branch of Chinese PLA General Hospital, Sanya, Hainan 572013, China
3Department of Radiology, The Fifth People's Hospital, Shizuishan, Ningxia 753000, China
4Department of Endocrinology, Hainan Branch of Chinese PLA General Hospital, Sanya, Hainan 572013, China
-
Received:2016-09-09Published:2017-06-30Online:2017-06-10 -
Contact:Ma Lin E-mail:cjr.malin@vip.163.com.
Cite this article
Chen Zhiye, Zang Xiujuan, Liu Mengqi, Liu Mengyu, Li Jinfeng, Gu Zhaoyan, Ma Lin. Abnormal Alterations of Cortical Thickness in 16 Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Pilot MRI Study△[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2017, 32(2): 75-82.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Table 1
Comparisons of mean cortical thickness of each brain region between T2DM patients and normal controls§"
| Brain lobe | Brain syrus | Cortical thickness(mm) | F value | P Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T2DM n=16 | NC n=16 | ||||
| Front lobe | L Paracentral | 2.50±0.12 | 2.65±0.13 | 13.16 | 0.001 |
| R Paracentral | 2.55±0.13 | 2.61±0.13 | 1.44 | 0.16 | |
| Parietal lobe | L postcentral | 2.16±0.09 | 2.21±0.11 | 6.03 | 0.02 |
| R postcentral | 2.14±0.12 | 2.21±0.14 | 4.75 | 0.04 | |
| Occipital lobe | L occipital gyrus | 2.28±0.11 | 2.83±0.13 | 4.72 | 0.04 |
| R occipital gyrus | 2.32±0.11 | 2.47±0.12 | 13.57 | 0.00 | |
| L lingual gyrus | 1.98±0.08 | 2.12±0.18 | 8.74 | 0.01 | |
| R lingual gyrus | 1.95±0.12 | 2.06±0.19 | 5.66 | 0.02 | |
| L precuneus cortex | 2.43±0.09 | 2.50±0.11 | 6.76 | 0.02 | |
| R precuneus cortex | 2.41±0.12 | 2.50±0.10 | 4.70 | 0.04 | |
| Temporal lobe | L inf. temporal gyrus | 2.89±0.12 | 2.99±0.13 | 6.30 | 0.02 |
| R inf. temporal gyrus | 2.83±0.13 | 2.93±0.18 | 7.07 | 0.01 | |
| L mid. temporal gyrus | 2.87±0.11 | 2.97±0.15 | 5.78 | 0.02 | |
| R mid. temporal gyrus | 2.85±0.13 | 2.97±0.11 | 11.32 | 0.001 | |
| L sup. temporal gyrus | 2.63±0.11 | 2.71±0.15 | 1.75 | 0.09 | |
| R sup. temporal gyrus | 2.65±0.13 | 2.79±0.12 | 11.94 | 0.001 | |
| L fusiform gyrus | 2.77±0.11 | 2.81±0.14 | 0.90 | 0.37 | |
| R fusiform gyrus | 2.64±0.14 | 2.80±0.15 | 9.04 | 0.01 | |
| Limbic system | L post. Cingulate gyrus | 2.70±0.11 | 2.82±0.13 | 8.12 | 0.01 |
| R post. Cingulate gyrus | 2.64±0.14 | 2.84±0.10 | 12.33 | 0.001 | |
| L isthmus of cingulate | 2.56±0.16 | 2.61±0.20 | 0.79 | 0.43 | |
| R isthmus of cingulate | 2.43±0.16 | 2.60±0.20 | 4.52 | 0.04 | |
| L insular cortex | 2.99±0.18 | 3.06±0.19 | 1.10 | 0.28 | |
| R insular cortex | 2.93±0.14 | 3.09±0.17 | 8.60 | 0.01 | |
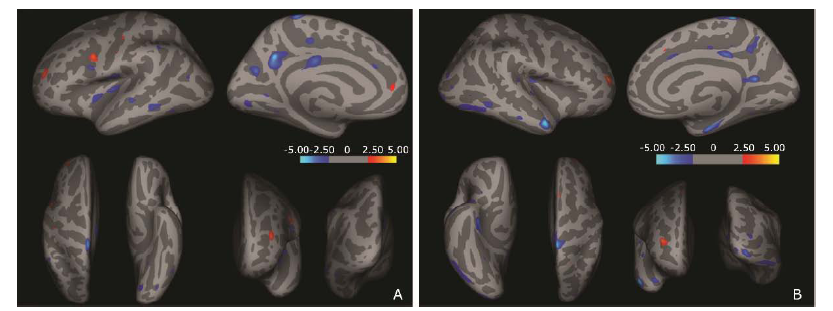
Figure 2.
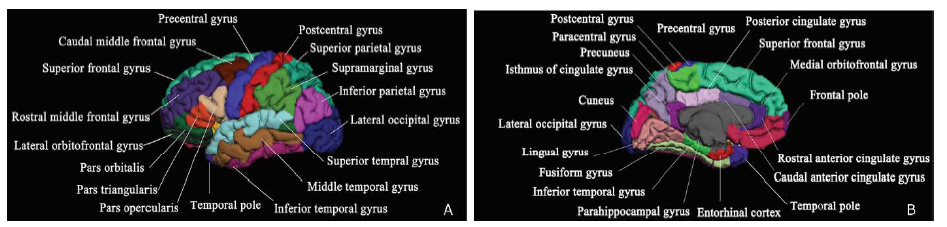
Regional cortical changes analyzed with surface-based cortical thickness in the brain of patients with T2DM compared with normal controls. Dark gray areas on the inflated cortical surface represent the sulci, light gray areas represent the gyri, and the color scale bar is on a -log (P value). Red clusters show that cortical thickness was thicker in diabetic patients than that of the normal controls. Blue clusters show that cortical thickness was thinner in the patients than that of normal controls.A.Left hemisphere: Brain regions with regional thickening are located in precentral gyrus, postcentral gyrus, rostral middle frontal gyrus and superior frontal gyrus; brain regions with regional thinning are located in precentral gyrus, postcentral gyrus, superior temporal gyrus, middle temporal gyrus, inferior temporal gyrus, inferior parietal lobule, paracentral lobule, superior frontal gyrus, posterior cingulate gyrus, precuneus, lingual gyrus and lateral occipital gyrus. B.Right hemisphere: Brain regions with regional thickening are located in superior frontal gyrus and rostral middle frontal gyrus; brain regions with regional thinning are located in postcentral gyrus, superior temporal gyrus, transverse temporal gyrus, middle temporal gyrus, inferior temporal gyrus, lateral occipital gyrus, precuneus, posterior cingulate gyrus, caudal anterior cingulate and entorhinal."
| 1. | Brands AM, Biessels GJ, de Haan EH, et al. The effects of type 1 diabetes on cognitive performance: a meta- analysis. Diabetes Care 2005; 28:726-35. doi:10.2337/ diacare.28.3.726. |
| 2. | Cukierman T, Gerstein HC, Williamson JD.Cognitive decline and dementia in diabetes-systematic overview of prospective observational studies. Diabetologia 2005; 48:2460-9. doi:10.1007/s00125-005-0023-4. |
| 3. | Allen KV, Frier BM, Strachan MW.The relationship between type 2 diabetes and cognitive dysfunction: longitudinal studies and their methodological limitations. Eur J Pharmacol 2004; 490:169-75. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar. 2004.02.054. |
| 4. | Scheltens P, Pasquier F, Weerts JG, et al.Qualitative assessment of cerebral atrophy on MRI: inter and intra- observer reproducibility in dementia and normal aging. Eur Neurol 1997; 37:95-9. DOI:10.1159/000117417. |
| 5. | de Bresser J, Tiehuis AM, van den Berg E, et al. Progression of cerebral atrophy and white matter hyperintensities in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2010; 33:1309-14. doi:10.2337/dc09-1923. |
| 6. | Gold SM, Dziobek I, Sweat V, et al.Hippocampal damage and memory impairments as possible early brain complications of type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2007; 50:711-9. doi:10.1007/s00125-007-0602-7. |
| 7. | Chen Z, Li L, Sun J, et al.Mapping the brain in type Ⅱ diabetes: Voxel-based morphometry using DARTEL. Eur J Radiol 2012; 81:1870-6. doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2011. 04.025. |
| 8. | Fischl B, Dale AM.Measuring the thickness of the human cerebral cortex from magnetic resonance images. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000; 97:11050-5. DOI:10.1073/pnas. 200033797. |
| 9. | MacDonald D, Kabani N, Avis D, et al. Automated 3-D extraction of inner and outer surfaces of cerebral cortex from MRI. Neuroimage 2000; 12: 340-56. DOI:10.1006/nimg. 1999.0534. |
| 10. | Miller MI, Massie AB, Ratnanather JT, et al.Bayesian construction of geometrically based cortical thickness metrics. Neuroimage 2000; 12: 676-87. doi:10.1006/ nimg.2000.0666. |
| 11. | Jones SE, Buchbinder BR, Aharon I.Three-dimensional mapping of cortical thickness using Laplace's equation. Hum Brain Mapp 2000; 11: 12-32. doi:10.1002/1097-0193 (200009)11:1%3C12:AID-HBM20%3E3.0.CO;2-K. |
| 12. | Hutton C, De Vita E, Ashburner J, et al.Voxel-based cortical thickness measurements in MRI. Neuroimage 2008; 40:1701-10. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.01.027. |
| 13. | Lebedev AV, Westman E, Beyer MK, et al.Multivariate classification of patients with Alzheimer's and dementia with Lewy bodies using high-dimensional cortical thickness measurements: an MRI surface-based morphometric study. J Neurol 2012; 260:1104-15. doi:10.1007/ s00415- 012-6768-z. |
| 14. | Qiu A, Gan SC, Wang Y, et al.Amygdala-hippocampal shape and cortical thickness abnormalities in first-episode schizophrenia and mania. Psychol Med 2012;43:1353-63. doi:10.1017/S0033291712002218. |
| 15. | Peng B, Chen Z, Ma L, et al.Cerebral alterations of type 2 diabetes mellitus on MRI: A pilot study. Neurosci Lett 2015; 606:100-5. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2015.08.030. |
| 16. | American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2009; 32 Suppl 1:S62-67. doi:10.2337/dc09-S062. |
| 17. | Manolio TA, Kronmal RA, Burke GL, et al.Magnetic resonance abnormalities and cardiovascular disease in older adults. The Cardiovascular Health Study. Stroke 1994; 25:318-27. doi:10.1161/01.STR.25.2.318. |
| 18. | Galea M, Woodward M.Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE). Aust J Physiother 2005; 51:198. doi:10.1016/ S0004-9514(05)70034-9. |
| 19. | Chen ZY, Sun J, Yang Y, et al.Cortical thinning in type 2 diabetes mellitus and the recovering effect of insulin therapy. J Clin Neurosci; 2015; 22:275-9. doi:10.1016/j. jocn.2014. 07.014. |
| 20. | Sled JG, Zijdenbos AP, Evans AC.A nonparametric method for automatic correction of intensity nonuniformity in MRI data. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 1998; 17: 87-97. doi:10.1109/42.668698. |
| 21. | Segonne F, Dale AM, Busa E, et al.A hybrid approach to the skull stripping problem in MRI. Neuroimage 2004; 22:1060-75. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.03.032. |
| 22. | Fischl B, Salat DH, van der Kouwe AJ, et al. Sequence- independent segmentation of magnetic resonance images. Neuroimage 2004; 23 Suppl 1:S69-84. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.07.016. |
| 23. | Fischl B, Salat DH, Busa E, et al.Whole brain segmentation: automated labeling of neuroanatomical structures in the human brain. Neuron 2002; 33:341-55. doi:10.1016/ S0896-6273(02)00569-X. |
| 24. | Fischl B, Sereno MI, Dale AM.Cortical surface-based analysis. Ⅱ: Inflation, flattening, and a surface-based coordinate system. Neuroimage 1999; 9:195-207. doi:10. 1006/nimg.1998.0396. |
| 25. | Fischl B, Sereno MI, Tootell RB, et al.High-resolution intersubject averaging and a coordinate system for the cortical surface. Hum Brain Mapp 1999; 8: 272-84. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0193(1999)8:4%3C272:AID-HBM10%3E3.0.CO;2-4. |
| 26. | Desikan RS, Segonne F, Fischl B, et al.An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on MRI scans into gyral based regions of interest. Neuroimage 2006; 31: 968-80. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage. 2006.01.021. |
| 27. | Brundel M, van den Heuvel M, de Bresser J, et al. Cerebral cortical thickness in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Neurol Sci 2010; 299: 126-30. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2010.08.048. |
| [1] | Atefeh Beigi-khoozani, Amirmohammad Merajikhah, Mahdieh Soleimani. Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings of Olfactory Bulb in Anosmic Patients with COVID-19: A Systematic Review [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2022, 37(1): 23-30. |
| [2] | Kunrong Wu, Shufang Zhang, Ziwan Guan, Xiaoli Li, Rui Li, Ying Yin, Yan Li. Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase Gene Polymorphism C677T is Associated with Increased Risk of Coronary Heart Disease in Chinese Type 2 Diabetic Patients [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(2): 103-109. |
| [3] | Jia Xu, Xuan Wang, Zhengyu Jin, Qin Wang, Yan You, Shitian Wang, Tianyi Qian, Huadan Xue. Assessing Liver Function by T1 Maps on Gd-EOB-DTPA-Enhanced MRI for up to 50 Min in Rat Models of Liver Fibrosis: A Longer Hepatobiliary Time Period may Help [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(2): 110-119. |
| [4] | Wang Xuedan, Wang Shiwei, Wang Botao, Chen Zhiye. Effect of MR Field Strength on the Texture Features of Cerebral T2-FLAIR Images: A Pilot Study [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(3): 248-253. |
| [5] | Xu Yanhong,Yang Jia,Meng Jie,Wang Han. Targeted MR Imaging Adopting T1-Weighted Ultra-Small Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Early Hepatocellular Carcinoma: An in vitro and in vivo Study [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(2): 142-150. |
| [6] | Yin Ying, Li Rui, Li Xiaoli, Wu Kunrong, Li Ling, Xu Yuedong, Liao Lin, Yang Rui, Li Yan. Association Between Homocysteine Level and Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase Gene Polymorphisms in Type 2 Diabetes Accompanied by Dyslipidemia [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(1): 85-91. |
| [7] | Sun Liang,Zhang Li,Zhang Daoqiang. Multi-Atlas Based Methods in Brain MR Image Segmentation [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(2): 110-119. |
| [8] | Guan Jian. Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare and Medicine: Promises, Ethical Challenges and Governance [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(2): 76-83. |
| [9] | Xu Jia, Wang Xuan, Jin Zhengyu, You Yan, Wang Qin, Wang Shitian, Xue Huadan. Value of Texture Analysis on Gadoxetic Acid-enhanced MR for Detecting Liver Fibrosis in a Rat Model [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 24-32. |
| [10] | Wang Botao, Fan Wenping, Xu Huan, Li Lihui, Zhang Xiaohuan, Wang Kun, Liu Mengqi, You Junhao, Chen Zhiye. Value of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Texture Analysis in the Differential Diagnosis of Benign and Malignant Breast Tumors [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 33-37. |
| [11] | Li Ping, Zhu Liang, Wang Xuan, Xue Huadan, Wu Xin, Jin Zhengyu. Imaging Diagnosis of Type Ⅲ Choledochal Cyst: A Case Report [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(3): 194-203. |
| [12] | Li Lihui, Huang Houbin, Chen Zhiye. Early Diagnosis of Recurrent Optic Neuritis Using Contrast-Enhanced T2 Fluid-attenuated Inversion Recovery Imaging: a Case Report [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(2): 130-134. |
| [13] | Chen Zhiye, Liu Mengqi, Ma Lin. Cortical Thinning Pattern of Bulbar- and Spinal-onset Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: a Surface-based Morphometry Study [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(2): 100-106. |
| [14] | Chen Zhiye,Liu Mengqi,Ma Lin. Gray Matter Volume Changes over the Whole Brain in the Bulbar- and Spinal-onset Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: a Voxel-based Morphometry Study [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(1): 20-28. |
| [15] | Liu Yang,Liu Ziyuan,Wan Xinhua,Guo Yi. Progress in the Diagnosis and Management of Chorea-acanthocytosis [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(1): 53-59. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|