Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2019, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (1): 1-9.doi: 10.24920/003531
• Original Articles • Next Articles
Value of Texture Analysis of Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Parameters in Differential Diagnosis of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor and Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma
Wang Yingwei1, 2, Zhang Xinghua2, Wang Botao1, Wang Ye2, Liu Mengqi1, 2, Wang Haiyi1, Ye Huiyi2, *( ), Chen Zhiye1, 2, *(
), Chen Zhiye1, 2, *( )
)
- 1 Department of Radiology, Hainan Hospital of Chinese PLA General Hospital, Sanya, Hainan 572013, China
2 Department of Radiology, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100853, China
-
Received:2018-10-18Revised:2019-02-22Published:2019-03-30Online:2019-04-08 -
Contact:Ye Huiyi,Chen Zhiye E-mail:13701100368@163.com;yyqf@hotmail.com
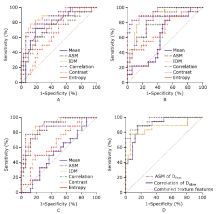
| This study was designed to investigate the capacity of the texture features derived from intravoxel incoherent motion parameters to differentiate pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor from pancreatic adenocarcinoma. And the Figure shown here revealed texture feature Angular Second Moment (ASM) of fast component of diffusion (Dfast) combined with Correlation of true diffusion parameter slow component of diffusion (Dslow) presented the excellent differential diagnostic performance between pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor and pancreatic adenocarcinoma (AUC 0.934, cutoff 0.378, sensitivity 0.889, specificity 0.854). |
Cite this article
Wang Yingwei, Zhang Xinghua, Wang Botao, Wang Ye, Liu Mengqi, Wang Haiyi, Ye Huiyi, Chen Zhiye. Value of Texture Analysis of Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Parameters in Differential Diagnosis of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor and Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 1-9.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
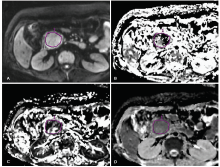
Figure 1.
IVIM parameters measurement of the lesion. A ROI was drawn on the lesion with maximal area on DW image (A), and the mimic ROI was automatically generated on parameter f map (B), Dfast map (C) and Dslow map (D) on the corresponding location. IVIM: intravoxel incoherent motion; ROI: region of interest; f: perfusion fraction; Dfast: fast component of diffusion; Dslow: true diffusion parameter slow component of diffusion."
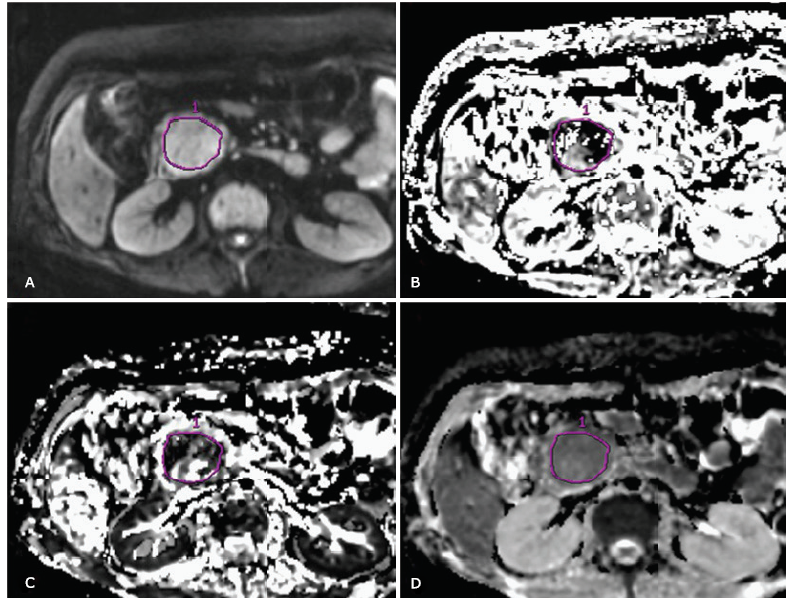
Table 1
Comparisons of texture features of IVIM parameters between the pNET and PAC groups"
| Parameters | PAC (n=32) | pNET (n=18) | U/t value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| f | ||||
| ASM | 0.398 (0.047) | 0.468 (0.079) | -4.224 | 0.000 |
| IDM | 0.779±0.032 | 0.806±0.033 | -2.810 | 0.007 |
| Correlation (x10-3) | 0.065±0.007 | 0.076±0.009 | -4.954 | 0.000 |
| Contrast | 4367.155 (1740.747) | 3785.633 (1.70.172) | -2.021 | 0.043 |
| Entropy | 2.294±0.173 | 2.080±0.234 | 3.687 | 0.001 |
| Dfast | ||||
| ASM | 0.350±0.049 | 0.450±0.623 | -6.283 | 0.000 |
| IDM | 0.701 (0.069) | 0.740 (0.045) | -3.456 | 0.001 |
| Correlation (x10-3) | 0.083±0.007 | 0.102±0.016 | -5.905 | 0.000 |
| Contrast | 2961.827±514.595 | 2469.961±618.127 | 3.016 | 0.004 |
| Entropy | 3.398 (0.587) | 2.947 (0.534) | -4.143 | 0.000 |
| Dslow | ||||
| ASM | 0.315±0.049 | 0.407±0.053 | -6.169 | 0.000 |
| IDM | 0.589±0.048 | 0.659±0.044 | -5.129 | 0.000 |
| Correlation (x10-3) | 0.198±0.034 | 0.269±0.057 | -5.562 | 0.000 |
| Contrast | 483.639±97.783 | 422.838±97.344 | 2.114 | 0.040 |
| Entropy | 4.570±0.441 | 3.833±0.421 | 5.768 | 0.000 |
Table 2
Binary Logistic regression analysis of texture features between the pNET group and PAC group"
| Independent variables | Regression coefficient | Standard error | Wald χ | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASM of Dfast | 35.251 | 13.929 | 6.405 | 0.011 |
| Correlation of Dslow | 33 247.973 | 14 163.943 | 5.510 | 0.019 |
| Constant | -22.112 | 7.255 | 9.289 | 0.002 |
Table 3
ROC analysis of mean value of IVIM parameters, texture features and combined texture features (ASM of Dfast and Correlation of Dslow) with logistic regression for differentiating pNET from PAC"
| Parameters | AUC | 95%CI | Cut-off value | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| f | |||||
| Mean value | 0.776 | 0.636-0.882 | 25.700a | 0.772 | 0.812 |
| ASM | 0.863 | 0.736-0.944 | 0.439a | 0.778 | 0.875 |
| IDM | 0.715 | 0.570-0.834 | 0.802a | 0.611 | 0.781 |
| Correlation | 0.849 | 0.719-0.934 | 0.069a | 0.778 | 0.812 |
| Contrast | 0.674 | 0.526-0.799 | 4675.279b | 1.000 | 0.406 |
| Entropy | 0.762 | 0.621-0.871 | 2.313b | 0.833 | 0.594 |
| Dfast | |||||
| Mean value | 0.611 | 0.463-0.746 | 28.000a | 0.833 | 0.500 |
| ASM | 0.899 | 0.781-0.966 | 0.389a | 0.889 | 0.844 |
| IDM | 0.797 | 0.659-0.897 | 0.727a | 0.778 | 0.750 |
| Correlation | 0.887 | 0.766-0.959 | 0.094a | 0.833 | 0.937 |
| Contrast | 0.724 | 0.579-0.841 | 2224.521b | 0.444 | 0.937 |
| Entropy | 0.856 | 0.718-0.939 | 3.231b | 0.944 | 0.656 |
| Dslow | |||||
| Mean value | 0.526 | 0.380-0.669 | 0.900 | 1.000 | 0.125 |
| ASM | 0.898 | 0.779-0.965 | 0.348a | 0.889 | 0.812 |
| IDM | 0.858 | 0.730-0.940 | 0.636a | 0.722 | 0.875 |
| Correlation | 0.856 | 0.728-0.939 | 0.245a | 0.778 | 0.937 |
| Contrast | 0.667 | 0.519-0.794 | 401.811b | 0.500 | 0.812 |
| Entropy | 0.880 | 0.757-0.955 | 4.218b | 0.889 | 0.750 |
| Combined texture features | 0.934 | 0.826-0.985 | 0.378a | 0.889 | 0.854 |
| 1. |
Dasari A, Shen C, Halperin D , et al. Trends in the incidence, prevalence, and survival outcomes in patients with neuroendocrine tumors in the United States. JAMA Oncol 2017; 3(10):1335-42. doi: 10.1001/ jamaoncol.2017.0589.
doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.0589 pmid: 28448665 |
| 2. |
Saif MW . Pancreatic neoplasm in 2011: an update. Jop 2011; 12(4):316-21.
doi: 10.6092/1590-8577/721 pmid: 21737886 |
| 3. |
Wong KP, Tsang JS, Lang BH . Role of surgery in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor. Gland Surg 2018; 7(1):36-41. doi: 10.21037/gs.2017.12.05
doi: 10.21037/gs.2017.12.05 pmid: 29629318 |
| 4. |
Clancy TE . Surgical management of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 2016; 30(1):103-18. doi: 10.1016/j.hoc.2015.09.004.
doi: 10.1016/j.soc.2015.12.002 pmid: 27013372 |
| 5. |
Doi R . Determinants of surgical resection for pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci 2015; 22(8):610-7. doi: 10.1002/jhbp.224.
doi: 10.1002/jhbp.224 pmid: 25773163 |
| 6. |
Chua TC, Yang TX, Gill AJ , et al. Systematic review and Meta-analysis of enucleation versus standardized resection for small pancreatic lesions. Ann Surg Oncol 2016; 23(2):592-9. doi: 10.1245/s10434-015-4826-3.
doi: 10.1245/s10434-015-4826-3 pmid: 26307231 |
| 7. |
Bednar F, Simeone DM . Recent advances in pancreatic surgery. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 2014; 30(5):518-23. doi: 10.1097/mog.0000000000000096.
doi: 10.1097/MOG.0000000000000096 pmid: 25010685 |
| 8. |
Lewis RB, Lattin GE , Jr., Paal E. Pancreatic endocrine tumors: radiologic-clinicopathologic correlation. Radiographics 2010; 30(6):1445-64. doi: 10.1148/rg.306105523.
doi: 10.1148/rg.306105523 pmid: 21071369 |
| 9. |
Manfredi R, Bonatti M, Mantovani W , et al. Non-hyperfunctioning neuroendocrine tumours of the pancreas: MR imaging appearance and correlation with their biological behaviour. Eur Radiol 2013; 23(11):3029-39. doi: 10.1007/s00330-013-2929-4.
doi: 10.1007/s00330-013-2929-4 pmid: 23793519 |
| 10. |
Iima M, Le Bihan D . Clinical intravoxel incoherent motion and diffusion MR imaging: past, present, and future. Radiology 2016; 278(1):13-32. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2015150244.
doi: 10.1148/radiol.2015150244 pmid: 26690990 |
| 11. |
Lee HJ, Rha SY, Chung YE , et al. Tumor perfusion-related parameter of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging: correlation with histological microvessel density. Magn Reson Med 2014; 71(4):1554-8. doi: 10.1002/mrm.24810.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.24810 pmid: 23798038 |
| 12. |
Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D , et al. Separation of diffusion and perfusion in intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging. Radiology 1988; 168(2):497-505. doi: 10.1148/radiology.168.2.3393671.
doi: 10.1148/radiology.168.2.3393671 pmid: 3393671 |
| 13. |
Ma W, Zhang G, Ren J , et al. Quantitative parameters of intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion weighted imaging (IVIM-DWI): potential application in predicting pathological grades of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Quant Imaging Med Surg 2018; 8(3):301-10. doi: 10.21037/qims.2018.04.08.
doi: 10.21037/qims.2018.04.08 pmid: 29774183 |
| 14. |
Ma C, Li Y, Wang L , et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion DWI of the pancreatic adenocarcinomas: monoexponential and biexponential apparent diffusion parameters and histopathological correlations. Cancer Imaging 2017; 17(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s40644-017-0114-8.
doi: 10.1186/s40644-017-0114-8 pmid: 5410078 |
| 15. |
Hwang EJ, Lee JM, Yoon JH , et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: prediction of the histologic grade using pure diffusion coefficient and tumor size. Invest Radiol 2014; 49(6):396-402. doi: 10.1097/rli.0000000000000028.
doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000028 |
| 16. |
Concia M, Sprinkart AM, Penner AH , et al. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of the pancreas: diagnostic benefit from an intravoxel incoherent motion model-based 3 b-value analysis. Invest Radiol 2014; 49(2):93-100. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0b013e3182a71cc3.
doi: 10.1097/RMR.0b013e3181b48667 pmid: 19687725 |
| 17. |
Klauss M, Lemke A, Grunberg K , et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion MRI for the differentiation between mass forming chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic carcinoma. Invest Radiol 2011; 46(1):57-63. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0b013e3181fb3bf2.
doi: 10.1097/RLI.0b013e3181fb3bf2 pmid: 21139505 |
| 18. |
Kang KM, Lee JM, Yoon JH , et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted MR imaging for characterization of focal pancreatic lesions. Radiology 2014; 270(2):444-53. doi: 10.1148/radiol.13122712.
doi: 10.1148/radiol.13122712 pmid: 24126370 |
| 19. |
Kim B, Lee SS, Sung YS , et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging of the pancreas: characterization of benign and malignant pancreatic pathologies. J Magn Reson Imaging 2017; 45(1):260-9. doi: 10.1002/jmri.25334.
doi: 10.1002/jmri.25334 pmid: 27273754 |
| 20. |
Klau M, Mayer P, Bergmann F , et al. Correlation of histological vessel characteristics and diffusion-weighted imaging intravoxel incoherent motion-derived parameters in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas and pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Invest Radiol 2015; 50(11):792-7. doi: 10.1097/rli.0000000000000187.
doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000187 pmid: 26186280 |
| 21. |
Li J, Liang L, Yu H , et al. Whole-tumor histogram analysis of non-Gaussian distribution DWI parameters to differentiation of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors from pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas. Magn Reson Imaging 2019; 55:52-9. doi: 10.1016/ j.mri.2018.09.017.
doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2018.09.017 |
| 22. | Wang BT, He L, Liu G , et al. Value of magnetic resonance imaging texture feature analysis in the differential diagnosis between pancreatic serous cystadenoma and mucinous cystadenoma. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao 2018; 40(2):187-93. doi: 10.3881/ j.issn.1000-503X.2018.02.008. |
| 23. |
Shindo T, Fukukura Y, Umanodan T , et al. Histogram analysis of apparent diffusion coefficient in differentiating pancreatic adenocarcinoma and neuroendocrine tumor. Medicine (Baltimore) 2016; 95(4):e2574. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000002574.
doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000002574 pmid: 5291570 |
| 24. |
Chen Z, Feng F, Yang Y , et al. MR imaging findings of the corpus callosum region in the differentiation between multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis optica. Eur J Radiol 2012; 81(11):3491-5. doi: 10.1016/ j.ejrad.2012.02.010.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2012.02.010 pmid: 22445592 |
| 25. |
Xia J, Broadhurst DI, Wilson M , et al. Translational biomarker discovery in clinical metabolomics: an introductory tutorial. Metabolomics 2013; 9(2):280-99. doi: 10.1007/s11306-012-0482-9.
doi: 10.1007/s11306-012-0482-9 |
| 26. |
Wu H, Liang Y, Jiang X , et al. Meta-analysis of intravoxel incoherent motion magnetic resonance imaging in differentiating focal lesions of the liver. Medicine (Baltimore) 2018; 97(34):e12071. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000012071.
doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000012071 |
| 27. | Mohanaiah P, Sathyanarayana P, Gurukumar L . Image texture feature extraction using GLCM approach. Inter J Sci Res Publications 2014; 3(5):1-5. |
| 28. |
Wang B, Liu G, Fan W , et al. Value of texture feature analysis in the differential diagnosis of hepatic cyst and hemangioma in magnetic resonance imaging. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao 2017; 39(2):169-76. doi: 10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.2017.02.002.
doi: 10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.2017.02.002 pmid: 28483013 |
| 29. |
Chen Z, Chen X, Liu M , et al. Magnetic resonance image texture analysis of the periaqueductal gray matter in episodic migraine patients without T2-visible lesions. Korean J Radiol 2018; 19(1):85. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2018.19.1.85.
doi: 10.3348/kjr.2018.19.1.85 |
| 30. |
Chen Z, Chen X, Chen Z , et al. Alteration of gray matter texture features over the whole brain in medication-overuse headache using a 3-dimentional texture analysis. J Headache Pain 2017; 18(1):112. doi: 10.1186/s10194-017-0820-4.
doi: 10.1186/s10194-017-0820-4 pmid: 29285575 |
| [1] | Liang Wang, Gang Li, Yun-tao Bing, Mao-lin Tian, Hangyan Wang, Chunhui Yuan, Dianrong Xiu. Does Prior Cancer Have an Influence on the Survival Outcomes of Patients with Localized Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors? [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(4): 284-294. |
| [2] | Gang Li, Yuntao Bing, Maolin Tian, Chunhui Yuan, Dianrong Xiu. Using a Nomogram to Preoperatively Predict Distant Metastasis of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor in Elderly Patients [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(3): 218-224. |
| [3] | Jian Cao, Guorong Wang, Zhiwei Wang, Zhengyu Jin. CT Texture Analysis: A Potential Biomarker for Evaluating KRAS Mutational Status in Colorectal Cancer [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(4): 306-314. |
| [4] | Wang Botao, Liu Mingxia, Chen Zhiye. Differential Diagnostic Value of Texture Feature Analysis of Magnetic Resonance T2 Weighted Imaging between Glioblastoma and Primary Central Neural System Lymphoma [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 10-17. |
| [5] | Liu Hongjuan, Zhou Huanfen, Zong Linxiong, Liu Mengqi, Wei Shihui, Chen Zhiye. MRI Histogram Texture Feature Analysis of the Optic Nerve in the Patients with Optic Neuritis [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 18-23. |
| [6] | Xu Jia, Wang Xuan, Jin Zhengyu, You Yan, Wang Qin, Wang Shitian, Xue Huadan. Value of Texture Analysis on Gadoxetic Acid-enhanced MR for Detecting Liver Fibrosis in a Rat Model [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 24-32. |
| [7] | Wang Botao, Fan Wenping, Xu Huan, Li Lihui, Zhang Xiaohuan, Wang Kun, Liu Mengqi, You Junhao, Chen Zhiye. Value of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Texture Analysis in the Differential Diagnosis of Benign and Malignant Breast Tumors [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 33-37. |
| [8] | Wang Guorong, Wang Zhiwei, Jin Zhengyu. Application and Progress of Texture Analysis in the Therapeutic Effect Prediction and Prognosis of Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy for Colorectal Cancer [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 45-50. |
| [9] | Yong-lan He, Da-ming Zhang, Hua-dan Xue*, Zheng-yu Jin. Clinical Value of Dual-energy CT in Detection of Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: Investigation of the Best Pancreatic Tumor Contrast to Noise Ratio [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2012, 27(4): 207-212. |
| [10] | Lin Lu, Feng Gu, Wei-xin Dai, Wu-yi Li, Jie Chen, Yu Xiao and Zheng-pei Zeng. Clinical and Pathological Features of Riedel‘s Thyroiditis [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2010, 25(3): 129-134. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|