Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2018, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (1): 20-28.doi: 10.24920/11804
延髓发病型及脊髓发病型肌萎缩侧索硬化症脑部磁共振结构特征变化
- 解放军总医院放射科,北京 100853
解放军总医院海南分院放射科,三亚 572013
-
收稿日期:2017-06-14出版日期:2018-02-13发布日期:2018-02-13 -
通讯作者:马林 E-mail:cjr.malin@vip.163.com
Gray Matter Volume Changes over the Whole Brain in the Bulbar- and Spinal-onset Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: a Voxel-based Morphometry Study
Chen Zhiye1,2,Liu Mengqi1,2,Ma Lin1,*( )
)
- 1 Department of Radiology, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100853, China
2 Department of Radiology, Hainan Branch of Chinese PLA General Hospital, Sanya, Hainan 572013, China
-
Received:2017-06-14Published:2018-02-13Online:2018-02-13 -
Contact:Ma Lin E-mail:cjr.malin@vip.163.com
摘要: 目的 采用基于体素的形态测量学技术探索延髓发病型及脊髓发病型肌萎缩侧索硬化症患者脑部磁共振成像结构特征。方法 对65例肌萎缩侧索硬化症患者(15例延髓型,50例脊髓型)及65名健康对照在3.0T磁共振扫描仪上行磁共振脑部结构成像。采用基于体素的形态测量学技术探索脑部灰质体积变化,采用神经形态学模版对体积变化脑区的体积进行计算。结果 与正常对照组比较,肌萎缩侧索硬化症患者在体素水平脑部灰质体积减少的脑区主要分布于右侧中央前回及额中回;延髓发病型肌萎缩侧索硬化症患者脑体积改变主要局限在运动皮层外萎缩(额-颞叶模式),而脊髓发病型肌萎缩侧索硬化症患者则主要表现为运动皮层萎缩(主要为右侧中央前回)及运动皮层外萎缩(额-颞叶模式及额-颞叶外模式)。两个肌萎缩侧索硬化症亚型间比较,脊髓发病型表现以左侧中央后回灰质体积减少为特征,延髓发病型表现以左侧颞中回灰质体积减少为特征。结论 运动皮层及运动皮层外灰质非对称性萎缩是脊髓发病型肌萎缩侧索硬化症患者脑部结构改变的特征,运动皮层外灰质萎缩是延髓发病型肌萎缩侧索硬化症患者脑部结构改变的特征。脊髓发病型灰质萎缩模式分布较延髓发病型更为广泛。
引用本文
Chen Zhiye,Liu Mengqi,Ma Lin. Gray Matter Volume Changes over the Whole Brain in the Bulbar- and Spinal-onset Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: a Voxel-based Morphometry Study[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(1): 20-28.
Table 1
Volume comparisons of rPrcGy, rMidFroGy, TGMV, TIV and fGMV between the ALS and NC groups (10-3 ml, n=65)"
| Groups | Volume of rPrcGy | Volume of rMidFroGy | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| means±SD | 95% CI | means±SD | 95% CI | ||||
| NCs | 12.14±1.33 | 11.68-12.30 | 18.71±2.41 | 17.84-18.97 | |||
| ALS | 11.36±1.34 | 11.19-11.81 | 17.64±2.61 | 17.38-18.51 | |||
| F value | 4.76 | 1.26 | |||||
| P value* | 0.03 | 0.27 | |||||
| Groups | TGMV | TIV | fGMV | ||||
| means±SD | 95% CI | means±SD | 95% CI | means±SD | 95% CI | ||
| NCs | 610.75±56.74 | 589.83-617.29 | 1423.72±127.38 | 1385.11-1453.02 | 0.43±0.02 | 0.42-0.43 | |
| ALS | 574.72±64.43 | 578.18-605.64 | 1393.96±144.74 | 1364.66-1432.57 | 0.42±0.02 | 0.41-0.43 | |
| F value | 1.36 | 0.69 | 0.41 | ||||
| P value* | 0.25 | 0.41 | 0.52 | ||||
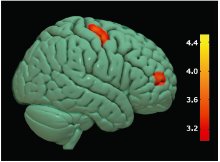
Figure 2.
Brain regions with decreased GM volume in bulbar-onset ALS patients compared with NC group. Colored areas represent the involved brain areas, including left medial orbital gyrus, left inferior temporal gyrus and right middle temporal gyrus group respectively. The value of the color bar represents T value."
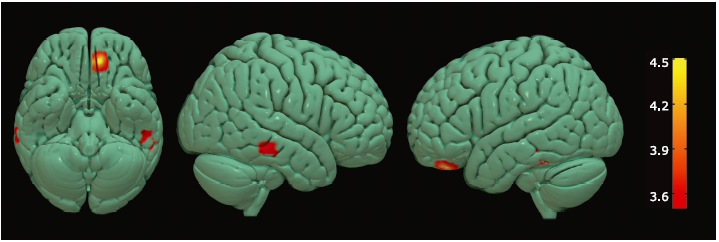
Table 2
Volume comparisons of the brain regions with decreased GMV and TGMV, TIV, fGMV between the ALS-bulbar and NC groups (10-3 ml)"
| Groups | n | Volume of lMedOrbGy | Volume of lInfTemGy | Volume of rMidTemGy | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| means±SD | 95% CI | means±SD | 95% CI | means±SD | 95% CI | ||
| NCs | 65 | 4.40±0.57 | 4.08-4.64 | 10.00±1.00 | 9.39-10.59 | 14.14±1.97 | 13.09-14.76 |
| bulbar-onset ALS | 15 | 4.15±0.51 | 3.91-4.47 | 8.94±1.17 | 8.35-9.55 | 13.49±1.46 | 12.87-14.54 |
| F value | 0.70 | 6.19 | 0.14 | ||||
| P value* | 0.41 | 0.02 | 0.71 | ||||
| Groups | n | TGMV | TIV | fGMV | |||
| means±SD | 95% CI | means±SD | 95% CI | means±SD | 95% CI | ||
| NCs | 65 | 610.75±56.74 | 589.83-617.29 | 1423.72±127.38 | 1385.11-1453.02 | 0.43±0.02 | 0.42-0.43 |
| bulbar-onset ALS | 15 | 577.18±65.12 | 554.32-614.58 | 1366.53±133.84 | 1309.04-1441.14 | 0.42±0.02 | 0.41-0.44 |
| F value | 0.07 | 0 | 0.32 | ||||
| P value* | 0.80 | 0.98 | 0.58 | ||||
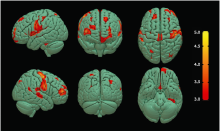
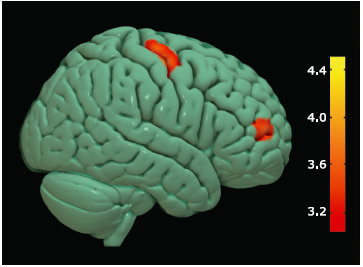
Figure 3.
Brain regions with decreased GM volume in ALS-spinal patients compared with NC group. Multiple colored areas represent the involved brain regions, including bilateral precentral gyrus (right precentral gyrus dominance) and the other multiple brain regions. The value of the color bar represents T value."

Table 3
Brain regions with decreased GM volume in patients with ALS-spinal compared with NCs"
| Anatomic region | MNI-space | K value | P value | T value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | Y | Z | ||||
| Left Thalamus Proper | -21 | -21 | 12 | 928 | 0.000 | 5.58 |
| Right Precentral Gyrus | 48 | -9 | 57 | 2753 | 0.000 | 5.46 |
| Left Superior Frontal Gyrus | -18 | 54 | 6 | 4582 | 0.000 | 5.35 |
| Left Postcentral Gyrus | -54 | -8 | 33 | 4032 | 0.000 | 5.15 |
| Right Middle Frontal Gyrus | 42 | 53 | 9 | 1015 | 0.000 | 4.88 |
| Left Central Operculum | -54 | 2 | 3 | 633 | 0.000 | 4.27 |
| Right Superior Frontal Gyrus | 23 | 54 | 21 | 351 | 0.000 | 4.24 |
| Right Middle Occipital Gyrus | 32 | -75 | 41 | 215 | 0.000 | 4.15 |
| Left Supramarginal Gyrus | -45 | -48 | 24 | 141 | 0.000 | 4.14 |
| Left Precuneus | -5 | -65 | 27 | 1157 | 0.000 | 4.06 |
| Left Middle Occipital Gyrus | -29 | -80 | 15 | 293 | 0.000 | 4.00 |
| Left Medial Precentral Gyrus | 0 | -18 | 75 | 220 | 0.000 | 3.97 |
| Right Superior Frontal Gyrus | 26 | 33 | 47 | 123 | 0.000 | 3.96 |
| Right Middle Temporal Gyrus | 60 | -20 | -8 | 274 | 0.000 | 3.95 |
| Right Angular Gyrus | 57 | -48 | 18 | 166 | 0.000 | 3.87 |
| Left Angular Gyrus | -48 | -60 | 35 | 153 | 0.000 | 3.78 |
| Left Inferior Frontal Angular Gyrus | -48 | 26 | 6 | 130 | 0.000 | 3.74 |
| Left Fusiform Gyrus | -32 | -33 | -29 | 177 | 0.000 | 3.70 |
| Left Superior Frontal Gyrus | -17 | 39 | 48 | 300 | 0.000 | 3.69 |
| Left Superior Parietal Lobule | -26 | -54 | 56 | 176 | 0.000 | 3.67 |

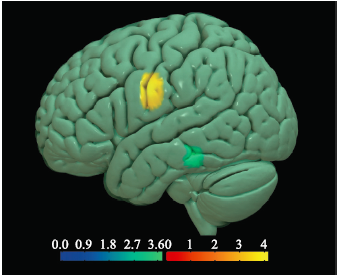
Figure 4.
Brain regions with altered volume of GM in the ALS-spinal and ALS-bulbar. Hot cluster in yellow, located in the left postcentral gyrus, represented the decreased volume in ALS-spinal compared with ALS-bulbar; cold cluster in green, located in the left middle temporal gyrus, represented decreased volume in ALS-bulbar compared with ALS-spinal."
| 1. |
van der Graaff MM, de Jong JM, Baas F, et al. Upper motor neuron and extra-motor neuron involvement in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a clinical and brain imaging review. Neuromuscul Disord,2009; 19(1): 53-8. doi:10.1016/j.nmd.2008.10.002.
doi: 10.1016/j.nmd.2008.10.002 pmid: 19070491 |
| 2. |
Hartung V, Prell T, Gaser C, et al. Voxel-based MRI intensitometry reveals extent of cerebral white matter pathology in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. PLoS One,2014; 9(8):e104894. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0104894.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104894 pmid: 25133577 |
| 3. |
Kalra S, Arnold D . Neuroimaging in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotrophic Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord,2003; 4(4):243-8. doi:10.1080/14660820310011269.
doi: 10.1080/14660820310011269 |
| 4. |
Grosskreutz J, Kaufmann J, Fr?drich J, et al. Widespread sensorimotor and frontal cortical atrophy in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. BMC Neurol,2006; 6:17. doi:10.1186/1471-2377-6-17.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2377-6-17 pmid: 1459868 |
| 5. |
Abrahams S, Goldstein LH, Suckling J, et al. Frontotemporal white matter changes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurol,2005; 252(3):321-31. doi:10.1007/s00415-005-0646-x.
doi: 10.1007/s00415-005-0646-x pmid: 15739047 |
| 6. |
Kassubek J, Unrath A, Huppertz HJ, et al. Global brain atrophy and corticospinal tract alterations in ALS, as investigated by voxel-based morphometry of 3-D MRI. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord,2005; 6(4):213-20. doi:10.1080/14660820510038538.
doi: 10.1080/14660820510038538 |
| 7. |
Yamauchi H, Fukuyama H, Ouchi Y, et al. Corpus callosum atrophy in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurol Sci,1995; 134(1-2):189-96. doi:10.1016/0022-510X(95)00220-6.
doi: 10.1016/0022-510X(95)00220-6 pmid: 8747865 |
| 8. |
Pinkhardt EH, van Elst LT, Ludolph AC, et al. Amygdala size in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis without dementia: an in vivo study using MRI volumetry. BMC Neurol,2006; 6:48. doi:10.1186/1471-2377-6-48.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2377-6-48 pmid: 1764753 |
| 9. |
Masuda M, Senda J, Watanabe H, et al. Involvement of the caudate nucleus head and its networks in sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-frontotemporal dementia continuum. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Frontotemporal Degener,2016; 17(7-8):571-9. doi:10.1080/21678421.2016.1211151.
doi: 10.1080/21678421.2016.1211151 pmid: 27684890 |
| 10. |
Mezzapesa DM, Ceccarelli A, Dicuonzo F, et al. Whole-brain and regional brain atrophy in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol,2007; 28(2):255-9. doi:10.1186/1471-2377-6-17.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2377-6-17 pmid: 17296989 |
| 11. |
Shen D, Cui L, Fang J, et al. Voxel-wise meta-analysis of gray matter changes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Front Aging Neurosci,2016; 8:64. doi:10.3389/fnagi.2016.00064.
doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2016.00064 pmid: 4811926 |
| 12. |
Sheng L, Ma H, Zhong J, et al. Motor and extra-motor gray matter atrophy in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: quantitative meta-analyses of voxel-based morphometry studies. Neurobiol Aging,2015; 36(12):3288-99. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2015.08.018.
doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2015.08.018 pmid: 26362941 |
| 13. |
Chen Z, Ma L . Grey matter volume changes over the whole brain in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a voxel-wise meta-analysis of voxel based morphometry studies. Amyotroph Lateral Scler,2010; 11(6):549-54. doi:10.3109/17482968.2010.516265.
doi: 10.3109/17482968.2010.516265 pmid: 20929296 |
| 14. |
Brooks BR , Miller RG , Swash M ,et al. . El Escorial ####: FFFF criteria for the diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord 2000; 1( 5): 293- 9. doi: 10.1080/146608200300079536.
doi: 10.1080/146608200300079536 pmid: 11464847 |
| 15. |
Swash M . New ideas on the ALS functional rating scale. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2017; 88( 5): 371- 2. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2016-315116.
doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2016-315116 pmid: 28039319 |
| 16. |
Herndon RM . Handbook of Neurologic Rating Scales. New York: Demos Vermande; 1997. p. 27- 79.
doi: 10.1136/jnnp.65.4.615a |
| 17. |
Galea M , Woodward M . Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE). Aust J Physiother 2005; 51( 3): 198. doi: 10.1016/S0004-9514(05)70034-9.
doi: 10.1016/S0004-9514(05)70034-9 |
| 18. |
Ashburner J , Friston KJ . Voxel-based morphometry—the methods. Neuroimage 2000; 11( 6 Pt 1): 805- 21. doi: 10.1006/nimg.2000.0582.
doi: 10.1006/nimg.2000.0582 |
| 19. |
Gredal O , Pakkenberg H , Karlsborg M ,et al. . Unchanged total number of neurons in motor cortex and neocortex in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a stereological study. J Neurosci Methods 2000; 95( 2): 171- 6. doi: 10.1016/S0165-0270(99)00175-2.
doi: 10.1016/S0165-0270(99)00175-2 pmid: 10752488 |
| 20. |
Kiernan JA , Hudson AJ . Changes in shapes of surviving motor neurons in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Brain 1993; 116( Pt 1): 203- 15. doi: 10.1093/brain/116.1.203.
doi: 10.1093/brain/116.1.203 pmid: 8453457 |
| 21. |
Schreiber H , Gaigalat T , Wiedemuth-Catrinescu U ,et al. . Cognitive function in bulbar- and spinal-onset amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. a longitudinal study in 52 patients. J Neurol 2005; 252( 7): 772- 81. doi: 10.1007/s00415-005-0739-6.
doi: 10.1007/s00415-005-0739-6 |
| 22. |
Butman JA , Floeter MK . Decreased thickness of primary motor cortex in primary lateral sclerosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2007; 28( 1): 87- 91.
doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-45456-4_43 pmid: 17213431 |
| 23. |
Roccatagliata L , Bonzano L , Mancardi G ,et al. . Detection of motor cortex thinning and corticospinal tract involvement by quantitative MRI in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph Lateral Scler 2009; 10( 1): 47- 52. doi: 10.1080/17482960802267530.
doi: 10.1080/17482960802267530 pmid: 1862277218622772 |
| 24. |
Chang JL , Lomen-Hoerth C , Murphy J ,et al. . A voxel-based morphometry study of patterns of brain atrophy in ALS and ALS/FTLD. Neurology 2005; 65( 1): 75- 80. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000167602.38643.29.
doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000167602.38643.29 |
| 25. |
Kato S , Hayashi H , Yagishita A . Involvement of the frontotemporal lobe and limbic system in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: as assessed by serial computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. J Neurol Sci 1993; 116( 1): 52- 8. doi: 10.1016/0022- 510X(93)90089-H.
doi: 10.1016/0022- 510X(93)90089-H pmid: 8509805 |
| 26. |
Hamilton RL , Bowser R . Alzheimer disease pathology in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol 2004; 107( 6): 515- 22. doi: 10.1007/s00401-004-0843-1.
doi: 10.1007/s00401-004-0843-1 pmid: 15024584 |
| 27. |
Hughes JT . Pathology of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Adv Neurol 1982; 36: 61- 74.
pmid: 7180695 |
| 28. |
Chan S , Shungu DC , Douglas-Akinwande A ,et al. . Motor neuron diseases: comparison of single-voxel proton MR spectroscopy of the motor cortex with MR imaging of the brain. Radiology 1999; 212( 3): 763- 9. doi: 10.1148/radiology.212.3.r99au35763.
doi: 10.1148/radiology.212.3.r99au35763 pmid: 10478245 |
| 29. |
Ellis CM , Suckling J , Amaro E , Jr., et al. Volumetric analysis reveals corticospinal tract degeneration and extramotor involvement in ALS. Neurology 2001; 57( 9): 1571- 8. doi: 10.1212/WNL.57.9.1571.
doi: 10.1212/WNL.57.9.1571 pmid: 11706094 |
| 30. |
Toft MH , Gredal O , Pakkenberg B . The size distribution of neurons in the motor cortex in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Anat 2005; 207( 4): 399- 407. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7580.2005.00465.x.
doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7580.2005.00465.x pmid: 16191168 |
| 31. |
Swick D , Ashley V , Turken AU . Left inferior frontal gyrus is critical for response inhibition. BMC Neurosci 2008; 9: 102. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-9-102.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-9-102 pmid: 18939997 |
| 32. |
Winhuisen L , Thiel A , Schumacher B ,et al. . Role of the contralateral inferior frontal gyrus in recovery of language function in poststroke aphasia: a combined repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation and positron emission tomography study. Stroke 2005; 36( 8): 1759- 63. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000174487.81126.ef.
doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000174487.81126.ef |
| 33. |
Zhu Z , Zhang JX , Wang S ,et al. . Involvement of left inferior frontal gyrus in sentence-level semantic integration. Neuroimage 2009; 47( 2): 756- 63. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.04.086.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.04.086 pmid: 19426814 |
| 34. |
Paulesu E , Goldacre B , Scifo P ,et al. . Functional heterogeneity of left inferior frontal cortex as revealed by fMRI. Neuroreport 1997; 8( 8): 2011- 7. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199705260-00042.
doi: 10.1097/00001756-199705260-00042 |
| 35. |
Lomen-Hoerth C , Murphy J , Langmore S ,et al. . Are amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients cognitively normal? Neurology 2003; 60( 7): 1094- 7. doi: 10.1212/01.WNL.0000055861.95202.8D.
doi: 10.1212/01.WNL.0000055861.95202.8D pmid: 12682312 |
| 36. |
Mantovan MC , Baggio L , Dalla Barba G , et al. Memory deficits and retrieval processes in ALS. Eur J Neurol 2003; 10( 3): 221- 7. doi: 10.1046/j.1468-1331.2003.00607.x.
doi: 10.1046/j.1468-1331.2003.00607.x pmid: 12752394 |
| 37. |
Abrahams S , Goldstein LH , Simmons A ,et al. . Word retrieval in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Brain 2004; 127( Pt 7): 1507- 17. doi: 10.1093/brain/awh170.
doi: 10.1093/brain/awh170 pmid: 15163610 |
| 38. |
Wijesekera LC , Leigh PN . Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Orphanet J Rare Dis 2009; 4: 3. doi: 10.1186/1750-1172-4-3.
doi: 10.1186/1750-1172-4-3 |
| 39. |
Portet F , Cadilhac C , Touchon J , Camu W . Cognitive impairment in motor neuron disease with bulbar onset. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord 2001; 2( 1): 23- 9. doi: 10.1080/14660820152415708.
doi: 10.1080/14660820152415708 pmid: 11465929 |
| [1] | 阿泰菲•贝吉•霍扎尼, 阿米尔穆罕默德•梅拉吉哈, 马赫迪耶•苏莱曼尼. 嗅觉缺失的新冠肺炎患者嗅球的磁共振成像结果:系统综述[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2022, 37(1): 23-30. |
| [2] | 徐佳, 王萱, 金征宇, 王勤, 游燕, 王士阗, 钱天翼, 薛华丹. 探索应用延长至50分钟的钆赛酸二钠增强磁共振T1 Maps评价大鼠肝纤维化模型肝功能的价值:延长的肝胆期可能提供帮助[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(2): 110-119. |
| [3] | 王雪丹, 王世伟, 王波涛, 陈志晔. 磁共振场强对脑T2-FLAIR图像纹理特征影响的初步研究[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(3): 248-253. |
| [4] | 王波涛, 刘明霞, 陈志晔. 磁共振T2加权成像纹理特征分析在脑胶质母细胞瘤与脑原发性中枢神经系统淋巴瘤鉴别诊断中的价值[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 10-17. |
| [5] | 徐佳, 王萱, 金征宇, 游燕, 王勤, 王士阗, 薛华丹. 钆塞酸二钠增强磁共振图像纹理分析对于评价大鼠肝纤维化的价值[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 24-32. |
| [6] | 王波涛, 樊文萍, 许欢, 李丽慧, 张晓欢, 王昆, 刘梦琦, 游俊浩, 陈志晔. 磁共振扩散加权成像纹理特征分析在乳腺良恶性肿瘤鉴别中的价值[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 33-37. |
| [7] | 李平, 朱亮, 王萱, 薛华丹, 吴晰, 金征宇. 影像学诊断1例III型胆总管囊肿[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(3): 194-203. |
| [8] | 陈志晔, 刘梦琦, 于生元, 马林. 多参数磁共振成像诊断小脑血管母细胞瘤1例报告[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(3): 188-193. |
| [9] | 陈志晔, 刘梦琦, 马林. 延髓发病型及脊髓发病型肌萎缩侧索硬化症患者皮层变薄模态:基于表面的形态学研究[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(2): 100-106. |
| [10] | 李丽慧, 黄厚斌, 陈志晔. 对比增强T2-FLAIR早期诊断复发性视神经炎一例报告[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(2): 130-134. |
| [11] | 刘梦琦, 陈志晔, 马林. 三维伪连续动脉自旋标记序列的可重复性:不同功能状态的健康成人在不同标记时间的脑容积灌注成像[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(1): 38-44. |
| [12] | 陈志晔, 刘梦琦, 马林. 基于表面的形态测量学:3T与7T高分辨磁共振结构成像受试者内比较[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2017, 32(4): 226-231. |
| [13] | 潘海鹏, 劳群, 费正华, 杨丽, 周海春, 赖灿. MR淋巴管造影诊断婴儿乳糜胸一例及文献回顾[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2017, 32(4): 265-268. |
| [14] | 陈志晔, 臧秀娟, 刘梦琦, 刘梦雨, 李金锋, 谷昭艳, 马林. 16例新发2型糖尿病患者脑部皮层厚度异常变化的MRI初步研究[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2017, 32(2): 75-82. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
|