Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2017, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (4): 265-268.doi: 10.24920/J1001-9294.2017.038
• Case Report • Previous Articles Next Articles
MR Lymphangiography for Focal Disruption of the Thoracic Duct in Chylothorax of an Infant: a Case Report and Literature Review△
Pan Haipeng1, 2, Lao Qun2, Fei Zhenghua3, Yang Li1, Zhou Haichun1, Lai Can1, *( )
)
- 1Department of Radiology, Children’s Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou 310052, China;
2Department of Radiology, Hangzhou Children’s Hospital, Hangzhou 310014, China;
3Department of Radiology, Huzhou Maternity & Child Care Hospital, Huzhou, Zhejiang 313000, China;
-
Received:2016-10-21Published:2017-12-30Online:2017-12-30 -
Contact:Lai Can E-mail:laican1000@163.com
Cite this article
Pan Haipeng, Lao Qun, Fei Zhenghua, Yang Li, Zhou Haichun, Lai Can. MR Lymphangiography for Focal Disruption of the Thoracic Duct in Chylothorax of an Infant: a Case Report and Literature Review△[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2017, 32(4): 265-268.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

Figure 1.
Multiple planar reconstruction (MPR) images showing the thoracic duct. A. Reconstructed coronal image of the magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP). The thoracic duct (arrow) presented hyperintense signal with approximate diameter of 4 mm at the levels of the 9th and 10th thoracic vertebrae, whereas the remaining thoracic duct was slender, presented a faint hyperintense signal with a diameter less than 1 mm. B. Reconstructed coronal image of the 3D gradient recalled echo sequence (GRE). Part of the thoracic duct (arrow) presented a mildly hyperintense signal."

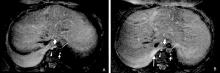
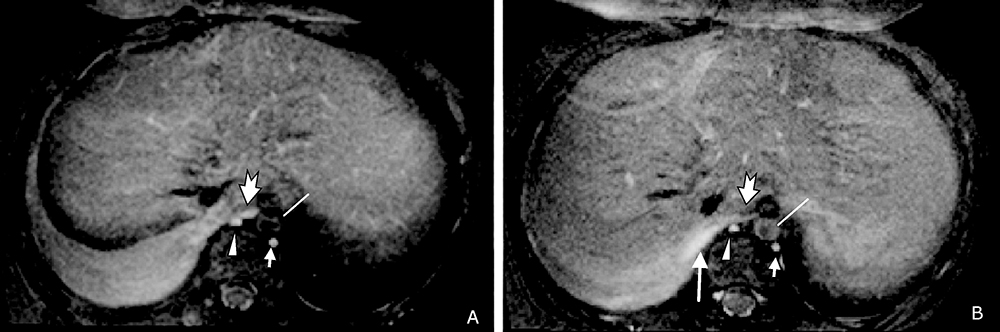
Figure 2.
Post-contrast spectral presaturation inversion recovery (SPIR) T1-weighted axial images at levels from the 9th (A) to the 10th (B) thoracic vertebra. A. The azygos vein (arrow head) and the hemiazygos vein (short arrow) were presented clearly beside the thoracic vertebrae. The thoracic duct (dovetail arrow) located between the azygos vein (arrow head) and the aorta (straight line), presenting slightly high signal intensity, with a larger diameter than that of azygos vein. B. A strip of hyperintense signal (long arrow) extended from the thoracic duct (dovetail arrow) to the right pleural effusion at the level of the 10th thoracic vertebra, demonstrating the site of chyle leakage."
| 1. | Yang J, Codreanu I, Zhuang H.Minimal lymphatic leakage in an infant with chylothorax detected by lymphoscintigraphy SPECT/CT. Pediatrics 2014; 134: e606-10. doi: 10.1542/peds.2013-2689. |
| 2. | Tan IC, Balaguru D, Rasmussen JC, Guilliod R, Bricker JT, Douglas WI, et al.Investigational lymphatic imaging at the bedside in a pediatric postoperative chylothorax patient. Pediatr Cardiol 2014; 35:1295-300. doi: 10.1007/s00246-014-0946-y. |
| 3. | Dori Y, Zviman MM, Itkin M.Dynamic contrast-enhanced MR lymphangiography: feasibility study in swine. Radiology 2014; 273:410-6. doi: 10.1148/radiol.14132616. |
| 4. | Kiryu S, Inoue Y, Sheng F, Watanabe M, Yoshikawa K, Shimada M, et al.Interstitial MR lymphography in mice: comparative study with gadofluorine 8, gadofluorine M, and gadofluorine P. Magn Reson Med Sci 2012; 11:99-107. doi: 10.2463/mrms.11.99. |
| 5. | Yu DX, Ma XX, Zhang XM, Wang Q, Li CF.Morphological features and clinical feasibility of thoracic duct: detection with nonenhanced magnetic resonance imaging at 3.0 T. J Magn Reson Imaging 2010; 32:94-100. doi: 10.1002/ jmri.22128. |
| 6. | Deso S, Ludwig B, Kabutey NK, Kim D, Guermazi A.Lymphangiography in the diagnosis and localization of various chyle leaks. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 2012; 35:117-26. doi: 10.1007/s00270-010-0066-x. |
| 7. | Ruehm SG, Schroeder T, Debatin JF.Interstitial MR lymphography with gadoterate meglumine: initial experience in humans. Radiology 2001; 220:816-21. doi: 10.1148/ radiol.2203010090 |
| 8. | Turkbey B, Kobayashi H, Hoyt RF Jr, Choyke PL, Naka-jima T, Griffiths GL, et al. Magnetic resonance lymphography of the thoracic duct after interstitial injection of gadofosveset trisodium: a pilot dosing study in a porcine model. Lymphat Res Biol 2014; 12: 32-6. doi: 10.1089/lrb.2013.0029. |
| [1] | Atefeh Beigi-khoozani, Amirmohammad Merajikhah, Mahdieh Soleimani. Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings of Olfactory Bulb in Anosmic Patients with COVID-19: A Systematic Review [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2022, 37(1): 23-30. |
| [2] | Jia Xu, Xuan Wang, Zhengyu Jin, Qin Wang, Yan You, Shitian Wang, Tianyi Qian, Huadan Xue. Assessing Liver Function by T1 Maps on Gd-EOB-DTPA-Enhanced MRI for up to 50 Min in Rat Models of Liver Fibrosis: A Longer Hepatobiliary Time Period may Help [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(2): 110-119. |
| [3] | Wang Xuedan, Wang Shiwei, Wang Botao, Chen Zhiye. Effect of MR Field Strength on the Texture Features of Cerebral T2-FLAIR Images: A Pilot Study [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(3): 248-253. |
| [4] | Xu Yanhong,Yang Jia,Meng Jie,Wang Han. Targeted MR Imaging Adopting T1-Weighted Ultra-Small Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Early Hepatocellular Carcinoma: An in vitro and in vivo Study [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(2): 142-150. |
| [5] | Xu Jia, Wang Xuan, Jin Zhengyu, You Yan, Wang Qin, Wang Shitian, Xue Huadan. Value of Texture Analysis on Gadoxetic Acid-enhanced MR for Detecting Liver Fibrosis in a Rat Model [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 24-32. |
| [6] | Wang Botao, Fan Wenping, Xu Huan, Li Lihui, Zhang Xiaohuan, Wang Kun, Liu Mengqi, You Junhao, Chen Zhiye. Value of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Texture Analysis in the Differential Diagnosis of Benign and Malignant Breast Tumors [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 33-37. |
| [7] | Li Ping, Zhu Liang, Wang Xuan, Xue Huadan, Wu Xin, Jin Zhengyu. Imaging Diagnosis of Type Ⅲ Choledochal Cyst: A Case Report [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(3): 194-203. |
| [8] | Chen Zhiye, Liu Mengqi, Ma Lin. Cortical Thinning Pattern of Bulbar- and Spinal-onset Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: a Surface-based Morphometry Study [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(2): 100-106. |
| [9] | Li Lihui, Huang Houbin, Chen Zhiye. Early Diagnosis of Recurrent Optic Neuritis Using Contrast-Enhanced T2 Fluid-attenuated Inversion Recovery Imaging: a Case Report [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(2): 130-134. |
| [10] | Chen Zhiye,Liu Mengqi,Ma Lin. Gray Matter Volume Changes over the Whole Brain in the Bulbar- and Spinal-onset Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: a Voxel-based Morphometry Study [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(1): 20-28. |
| [11] | Liu Mengqi, Chen Zhiye, Ma Lin. Reliability of Three Dimentional Pseudo-continuous Arterial Spin Labeling: A Volumetric Cerebral Perfusion Imaging with Different Post-labeling Time and Functional State in Health Adults [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(1): 38-44. |
| [12] | Chen Zhiye, Zang Xiujuan, Liu Mengqi, Liu Mengyu, Li Jinfeng, Gu Zhaoyan, Ma Lin. Abnormal Alterations of Cortical Thickness in 16 Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Pilot MRI Study△ [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2017, 32(2): 75-82. |
| [13] | Wang Ting, Ma Lin, Lou Xin, Bu Bo. Trigeminal Ganglioneuroma in the Middle-posterior Cranial Fossa: a Case Report△ [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2017, 32(2): 123-128. |
| [14] | Yu Wang, Zi-yuan Liu, Wan-chen Dou, Wen-bin Ma, Ren-zhi Wang, Yi Guo. Application of Preoperative CT/MRI Image Fusion in Target Positioning for Deep Brain Stimulation [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2016, 31(3): 161-167. |
| [15] | Xiang Quan, Tie-hu Ye, Si-fang Lin, Liang Zou, Shou-yuan Tian. Propofol Affects Different Human Brain Regions Depending on Depth of Sedation [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2015, 30(3): 135-142. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|

