Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (2): 110-119.doi: 10.24920/003794
探索应用延长至50分钟的钆赛酸二钠增强磁共振T1 Maps评价大鼠肝纤维化模型肝功能的价值:延长的肝胆期可能提供帮助
徐佳1,王萱1,*( ),金征宇1,*(
),金征宇1,*( ),王勤1,游燕2,王士阗1,钱天翼3,薛华丹1
),王勤1,游燕2,王士阗1,钱天翼3,薛华丹1
- 1中国医学科学院 北京协和医学院 北京协和医院放射科,北京 100730
2中国医学科学院 北京协和医学院 北京协和医院病理科,北京 100730
3西门子医疗系统有限公司,北京 100102
-
收稿日期:2020-09-15出版日期:2021-06-30 -
通讯作者:王萱,金征宇 E-mail:dr_wangxuan@163.com;jinzy@pumch.cn
Assessing Liver Function by T1 Maps on Gd-EOB-DTPA-Enhanced MRI for up to 50 Min in Rat Models of Liver Fibrosis: A Longer Hepatobiliary Time Period may Help
Jia Xu1,Xuan Wang1,*( ),Zhengyu Jin1,*(
),Zhengyu Jin1,*( ),Qin Wang1,Yan You2,Shitian Wang1,Tianyi Qian3,Huadan Xue1
),Qin Wang1,Yan You2,Shitian Wang1,Tianyi Qian3,Huadan Xue1
- 1Department of Radiology,Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100730, China
2Department of Pathology, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100730, China
3Siemens Healthcare Ltd., Beijing 100102, China
-
Received:2020-09-15Published:2021-06-30 -
Contact:Xuan Wang,Zhengyu Jin E-mail:dr_wangxuan@163.com;jinzy@pumch.cn
摘要:
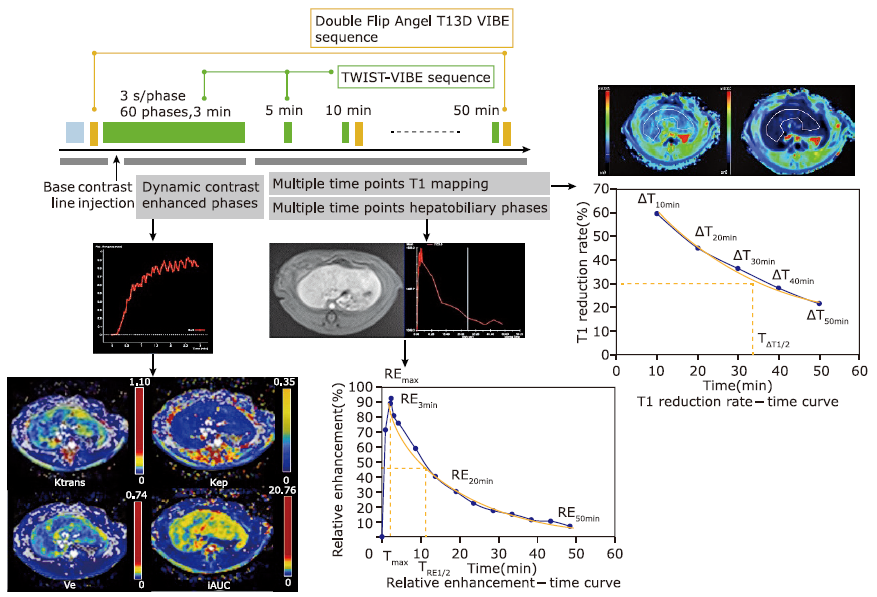
目的 探索延长成像时间的钆赛酸二钠(Gd-EOB-DTPA)增强磁共振T1 mapping成像及快速动态增强扫描序列(DCE)、多期肝胆期磁共振成像对于大鼠肝纤维模型肝功能的评价是否存在潜在价值。
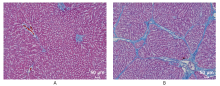
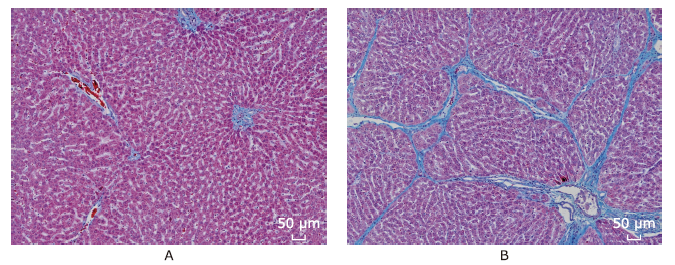
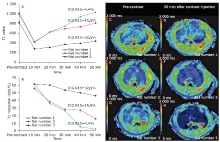
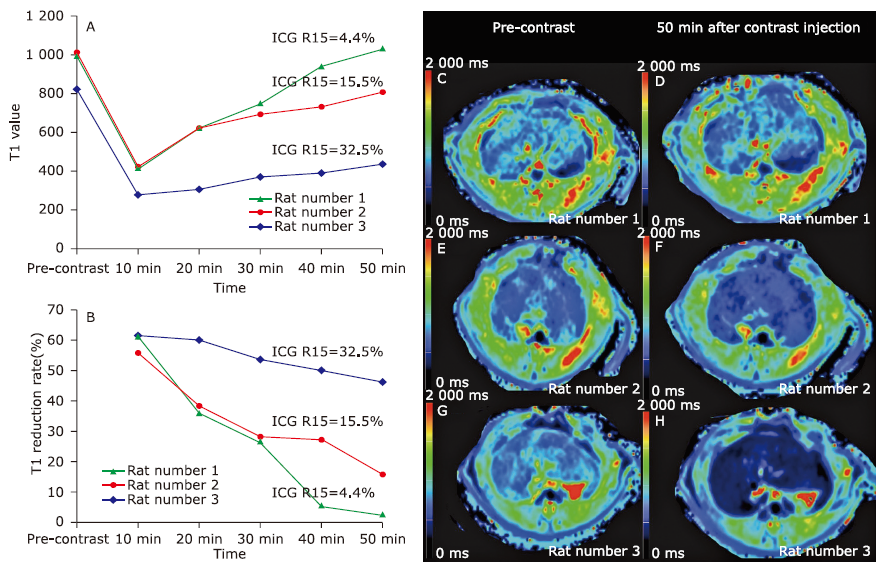
方法 40只雄性SD大鼠,分为采用四氯化碳溶液腹腔注射的肝功能损伤组[四氯化碳溶液分别注射4周(n=14)、8周(n=8)、12周(n=8)]以及对照组(n=10)。钆赛酸二钠磁共振增强扫描序列包括T1-mapping成像(延至注射对比剂后50分钟)、DCE、以及多期肝胆期成像。测量获得吲哚菁绿15分钟潴留率(ICG R15)。图像分析计算获得影像学参数如T1弛豫时间减低率(ΔT1)、ΔT1减半时间(TΔT1 1/2)、相对强化率(RE)、RE达峰时间(Tmax)、灌注参数等。应用Pearson相关性分析比较影像学参数与ICG R15的关系。
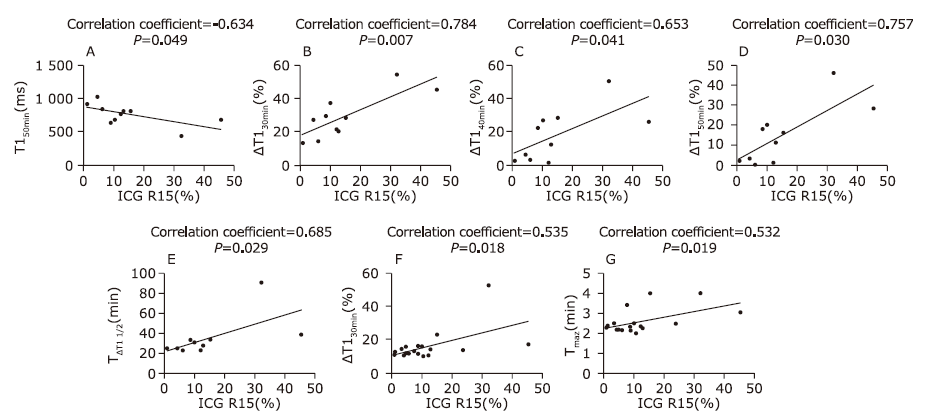
结果30、40、50分钟的ΔT1和ICG R15具有显著正相关性(r=0.784,0.653,0.757,P=0.007,0.041,0.030)。TΔT1 1/2与ICG R15具有显著正相关性(r=0.685,P=0.029)。Tmax与ICG R15具有显著正相关性(r=0.532,P=0.019)。
结论 晚期肝胆期的ΔT1及TΔT1 1/2与肝功能具有中度相关性。延长成像时间的钆赛酸二钠增强磁共振T1 mapping成像及DCE、多期肝胆期磁共振成像对于大鼠肝纤维模型肝功能的评价具有一定价值。
引用本文
Jia Xu, Xuan Wang, Zhengyu Jin, Qin Wang, Yan You, Shitian Wang, Tianyi Qian, Huadan Xue. Assessing Liver Function by T1 Maps on Gd-EOB-DTPA-Enhanced MRI for up to 50 Min in Rat Models of Liver Fibrosis: A Longer Hepatobiliary Time Period may Help[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2021, 36(2): 110-119.
| [1.] |
Hammond JS, Guha IN, Beckingham IJ, et al. Prediction, prevention and management of postresection liver failure. Br J Surg 2011; 98(9):1188-200. doi: 10.1002/bjs.7630.
doi: 10.1002/bjs.7630 pmid: 21725970 |
| [2.] |
Kudo M, Izumi N, Kokudo N, et al. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma in Japan: Consensus-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines proposed by the Japan Society of Hepatology (JSH) 2010 updated version. Dig Dis 2011; 29(3):339-64. doi: 10.1159/000327577.
doi: 10.1159/000327577 |
| [3.] |
Geisel D, Ludemann L, Hamm B, et al. Imaging-based liver function tests—past, present and future. Rofo 2015; 187(10):863-71. doi: 10.1055/s-0035-1553306.
doi: 10.1055/s-0035-1553306 pmid: 26230140 |
| [4.] |
Van Beers BE, Pastor CM, Hussain HK. Primovist, eovist: what to expect? J Hepatol 2012; 57(2):421-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2012.01.031.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2012.01.031 |
| [5.] |
Ba-Ssalamah A, Bastati N, Wibmer A, et al. Hepatic gadoxetic acid uptake as a measure of diffuse liver disease: where are we? J Magn Reson Imaging 2017; 45(3):646-59. doi: 10.1002/jmri.25518.
doi: 10.1002/jmri.25518 pmid: 27862590 |
| [6.] |
Motosugi U, Ichikawa T, Sou H, et al. Liver parenchymal enhancement of hepatocyte-phase images in Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MR imaging: which biological markers of the liver function affect the enhancement? J Magn Reson Imaging 2009; 30(5):1042-6. doi: 10.1002/jmri.21956.
doi: 10.1002/jmri.21956 pmid: 19856436 |
| [7.] |
Verloh N, Haimerl M, Zeman F, et al. Assessing liver function by liver enhancement during the hepatobiliary phase with Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI at 3 Tesla. Eur Radiol 2014; 24(5):1013-9. doi: 10.1007/s00330-014-3108-y.
doi: 10.1007/s00330-014-3108-y pmid: 24531844 |
| [8.] |
Sato Y, Matsushima S, Inaba Y, et al. Preoperative estimation of future remnant liver function following portal vein embolization using relative enhancement on gadoxetic acid disodium-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Korean J Radiol 2015; 16(3):523-30. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2015.16.3.523.
doi: 10.3348/kjr.2015.16.3.523 |
| [9.] |
Ippolito D, Pecorelli A, Famularo S, et al. Assessing liver function: diagnostic efficacy of parenchymal enhancement and liver volume ratio of Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI study during interstitial and hepatobiliary phase. Abdom Radiol (NY) 2019; 44(4):1340-9. doi: 10.1007/s00261-018-1812-9.
doi: 10.1007/s00261-018-1812-9 pmid: 30411177 |
| [10.] |
Ryeom HK, Kim SH, Kim JY, et al. Quantitative evaluation of liver function with MRI using Gd-EOB-DTPA. Korean J Radiol 2004; 5(4):231-9. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2004.5.4.231.
doi: 10.3348/kjr.2004.5.4.231 |
| [11.] |
Saito K, Ledsam J, Sourbron S, et al. Measuring hepatic functional reserve using low temporal resolution Gd-EOB-DTPA dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI: a preliminary study comparing galactosyl human serum albumin scintigraphy with indocyanine green retention. Eur Radiol 2014; 24(1):112-9. doi: 10.1007/s00330-013-2983-y.
doi: 10.1007/s00330-013-2983-y |
| [12.] |
Ning J, Yang Z, Xie S, et al. Hepatic function imaging using dynamic Gd-EOB-DTPA enhanced MRI and pharmacokinetic modeling. Magn Reson Med 2017; 78(4):1488-95. doi: 10.1002/mrm.26520.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.26520 pmid: 27785826 |
| [13.] |
Sourbron S, Sommer WH, Reiser MF, et al. Combined quantification of liver perfusion and function with dynamic gadoxetic acid-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology 2012; 263(3):874-83. doi: 10.1148/radiol.12110337.
doi: 10.1148/radiol.12110337 pmid: 22623698 |
| [14.] |
Katsube T, Okada M, Kumano S, et al. Estimation of liver function using T1 mapping on Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Invest Radiol 2011; 46(4):277-83. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0b013e318200f67d.
doi: 10.1097/RLI.0b013e318200f67d |
| [15.] |
Haimerl M, Verloh N, Zeman F, et al. Assessment of clinical signs of liver cirrhosis using T1 mapping on Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced 3T MRI. PLoS One 2013; 8(12):e85658. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085658.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085658 |
| [16.] |
Haimerl M, Verloh N, Fellner C, et al. MRI-based estimation of liver function: Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced T1 relaxometry of 3T vs. the MELD score . Sci Rep 2014; 4:5621. doi: 10.1038/srep05621.
doi: 10.1038/srep05621 |
| [17.] |
Kamimura K, Fukukura Y, Yoneyama T, et al. Quantitative evaluation of liver function with T1 relaxation time index on Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI: comparison with signal intensity-based indices. J Magn Reson Imaging 2014; 40(4):884-9. doi: 10.1002/jmri.24443.
doi: 10.1002/jmri.24443 |
| [18.] |
Zhou ZP, Long LL, Qiu WJ, et al. Comparison of 10- and 20-min hepatobiliary phase images on Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI T1 mapping for liver function assessment in clinic. Abdom Radiol (NY) 2017; 42(9):2272-8. doi: 10.1007/s00261-017-1143-2.
doi: 10.1007/s00261-017-1143-2 |
| [19.] |
Yoon JH, Lee JM, Kim E, et al. Quantitative liver function analysis: volumetric T1 mapping with fast multisection B1 inhomogeneity correction in hepatocyte-specific contrast-enhanced liver MR imaging. Radiology 2017; 282(2):408-17. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2016152800.
doi: 10.1148/radiol.2016152800 |
| [20.] |
Nakagawa M, Namimoto T, Shimizu K, et al. Measuring hepatic functional reserve using T1 mapping of Gd-EOB-DTPA enhanced 3T MR imaging: a preliminary study comparing with 99mTc GSA scintigraphy and signal intensity based parameters. Eur J Radiol 2017; 92:116-23. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2017.05.011.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2017.05.011 |
| [21.] |
Ding Y, Rao SX, Chen C, et al. Assessing liver function in patients with HBV-related HCC: a comparison of T(1) mapping on Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MR imaging with DWI. Eur Radiol 2015; 25(5):1392-8. doi: 10.1007/s00330-014-3542-x.
doi: 10.1007/s00330-014-3542-x |
| [22.] |
Yuan J, Chow SK, Yeung DK, et al. Quantitative evaluation of dual-flip-angle T1 mapping on DCE-MRI kinetic parameter estimation in head and neck. Quant Imaging Med Surg 2012; 2(4):245-53. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2223-4292.2012.11.04.
doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2223-4292.2012.11.04 |
| [23.] |
Kim KA, Herigault G, Kim MJ, et al. Three-dimensional contrast-enhanced hepatic MR imaging: comparison between a centric technique and a linear approach with partial Fourier along both slice and phase directions. J Magn Reson Imaging 2011; 33(1):160-6. doi: 10.1002/jmri.22436.
doi: 10.1002/jmri.22436 |
| [24.] |
Sheng RF, Wang HQ, Yang L, et al. Assessment of liver fibrosis using T1 mapping on Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced magnetic resonance. Dig Liver Dis 2017; 49(7):789-95. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2017.02.006.
doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2017.02.006 |
| [25.] |
Kundel HL, Polansky M. Measurement of observer agreement. Radiology 2003; 228(2):303-8. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2282011860.
doi: 10.1148/radiol.2282011860 |
| [26.] |
Zhou ZP, Long LL, Huang LJ, et al. Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI T1 mapping for assessment of liver function in rabbit fibrosis model: comparison of hepatobiliary phase images obtained at 10 and 20 min. Radiol Med 2017; 122(4):239-47. doi: 10.1007/s11547-016-0719-1.
doi: 10.1007/s11547-016-0719-1 |
| [27.] |
Haimerl M, Schlabeck M, Verloh N, et al. Volume-assisted estimation of liver function based on Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MR relaxometry. Eur Radiol 2016; 26(4):1125-33. doi: 10.1007/s00330-015-3919-5.
doi: 10.1007/s00330-015-3919-5 |
| [28.] |
Zhou ZP, Long LL, Qiu WJ, et al. Evaluating segmental liver function using T1 mapping on Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI with a 3.0 Tesla. BMC Med Imaging 2017; 17(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s12880-017-0192-x.
doi: 10.1186/s12880-017-0192-x |
| [29.] |
Unal E, Idilman IS, Karcaaltincaba M. Multiparametric or practical quantitative liver MRI: towards millisecond, fat fraction, kilopascal and function era. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2017; 11(2):167-82. doi: 10.1080/17474124.2017.1271710.
doi: 10.1080/17474124.2017.1271710 |
| [30.] |
Yoneyama T, Fukukura Y, Kamimura K, et al. Efficacy of liver parenchymal enhancement and liver volume to standard liver volume ratio on Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI for estimation of liver function. Eur Radiol 2014; 24(4):857-65. doi: 10.1007/s00330-013-3086-5.
doi: 10.1007/s00330-013-3086-5 |
| [31.] |
Tsuda N, Matsui O. Signal profile on Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MR imaging in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and liver cirrhosis induced in rats: correlation with transporter expression. Eur Radiol 2011; 21(12):2542-50. doi: 10.1007/s00330-011-2228-x.
doi: 10.1007/s00330-011-2228-x |
| [32.] |
Saito S, Obata A, Kashiwagi Y, et al. Dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI of the liver in Mrp2-deficient rats using the hepatobiliary contrast agent Gd-EOB-DTPA. Invest Radiol 2013; 48(7):548-53. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0b013e3182856a06.
doi: 10.1097/RLI.0b013e3182856a06 |
| [33.] |
Hinrichs H, Hinrichs JB, Gutberlet M, et al. Functional gadoxetate disodium-enhanced MRI in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC). Eur Radiol 2016; 26(4):1116-24. doi: 10.1007/s00330-015-3913-y.
doi: 10.1007/s00330-015-3913-y pmid: 26205638 |
| [34.] |
Yamada T, Kashiwagi Y, Rokugawa T, et al. Evaluation of hepatic function using dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in melanocortin 4 receptor-deficient mice as a model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Magn Reson Imaging 2019; 57:210-7. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2018.11.013.
doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2018.11.013 |
| [35.] |
Zhang W, Kong X, Wang ZJ, et al. Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging with Gd-EOB-DTPA for the evaluation of liver fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride in rats. PLoS One 2015; 10(6):e0129621. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0129621.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0129621 |
| [36.] |
Yang JF, Zhao ZH, Zhang Y, et al. Dual-input two-compartment pharmacokinetic model of dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(13):3652-62. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i13.3652.
doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i13.3652 |
| [1] | 阿泰菲•贝吉•霍扎尼, 阿米尔穆罕默德•梅拉吉哈, 马赫迪耶•苏莱曼尼. 嗅觉缺失的新冠肺炎患者嗅球的磁共振成像结果:系统综述[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2022, 37(1): 23-30. |
| [2] | 王雪丹, 王世伟, 王波涛, 陈志晔. 磁共振场强对脑T2-FLAIR图像纹理特征影响的初步研究[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2020, 35(3): 248-253. |
| [3] | 王波涛, 刘明霞, 陈志晔. 磁共振T2加权成像纹理特征分析在脑胶质母细胞瘤与脑原发性中枢神经系统淋巴瘤鉴别诊断中的价值[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 10-17. |
| [4] | 徐佳, 王萱, 金征宇, 游燕, 王勤, 王士阗, 薛华丹. 钆塞酸二钠增强磁共振图像纹理分析对于评价大鼠肝纤维化的价值[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 24-32. |
| [5] | 王波涛, 樊文萍, 许欢, 李丽慧, 张晓欢, 王昆, 刘梦琦, 游俊浩, 陈志晔. 磁共振扩散加权成像纹理特征分析在乳腺良恶性肿瘤鉴别中的价值[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2019, 34(1): 33-37. |
| [6] | 李平, 朱亮, 王萱, 薛华丹, 吴晰, 金征宇. 影像学诊断1例III型胆总管囊肿[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(3): 194-203. |
| [7] | 陈志晔, 刘梦琦, 于生元, 马林. 多参数磁共振成像诊断小脑血管母细胞瘤1例报告[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(3): 188-193. |
| [8] | 陈志晔, 刘梦琦, 马林. 延髓发病型及脊髓发病型肌萎缩侧索硬化症患者皮层变薄模态:基于表面的形态学研究[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(2): 100-106. |
| [9] | 李丽慧, 黄厚斌, 陈志晔. 对比增强T2-FLAIR早期诊断复发性视神经炎一例报告[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(2): 130-134. |
| [10] | 陈志晔,刘梦琦,马林. 延髓发病型及脊髓发病型肌萎缩侧索硬化症脑部磁共振结构特征变化[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(1): 20-28. |
| [11] | 刘梦琦, 陈志晔, 马林. 三维伪连续动脉自旋标记序列的可重复性:不同功能状态的健康成人在不同标记时间的脑容积灌注成像[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2018, 33(1): 38-44. |
| [12] | 陈志晔, 刘梦琦, 马林. 基于表面的形态测量学:3T与7T高分辨磁共振结构成像受试者内比较[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2017, 32(4): 226-231. |
| [13] | 潘海鹏, 劳群, 费正华, 杨丽, 周海春, 赖灿. MR淋巴管造影诊断婴儿乳糜胸一例及文献回顾[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2017, 32(4): 265-268. |
| [14] | 陈志晔, 臧秀娟, 刘梦琦, 刘梦雨, 李金锋, 谷昭艳, 马林. 16例新发2型糖尿病患者脑部皮层厚度异常变化的MRI初步研究[J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2017, 32(2): 75-82. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
|